在进行AI学习、统计的时候,通常用Matplotlib进行数据的可视化,本文总结下Matplotlib中基本用法,首先import matplotlib.pyplot as plt。
基本用法
Matplotlib可以绘制很多种类型的图,见底部参考,常见的是折线图,其次还有散点图、柱状图、条状图、饼图、动态图、3D图等。
折线图
先备注下常用api
fig = plt.figure() #开始画图
plt.plot(X, Y, 'b-', lw=2.5, label='label') #指定x、y轴坐标值,线宽、此条线名称
plt.legend(loc='upper left') # 注解位置
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max) # 设置x轴坐标轴范围,也可以通过ylim设置y轴范围
plt.xticks([x1, x2, x3, x4]) #设置x轴坐标轴刻度
plt.show() 显示图下表包含了plot可以使用的风格:
- | 实线(默认) | | + | 加号
-- | 虚线 || o | 圆圈
: | 点线 | | * | 星号
-. | 点划线 || . | 实心点
标记 | 颜色 || x | 叉
r | 红 | | s | 正方形
g | 绿 | | d | 钻石
b | 蓝 | | ^ | 上三角
c | 蓝绿 || v | 下三角
m | 紫红 | | < | 左三角
y | 黄 || > | 右三角
k | 黑 | | p | 正五角形
w | 白 || h | 正六角形
颜色除了预定义好的单个字母表示,还可以用color='#00ff00'或者color=(1.0, 0.5, 0.04)表示。
一个简单示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
# https://www.jianshu.com/p/8ed59ac76c06 中文显示问题
def getChineseFont():
return FontProperties(fname='/System/Library/Fonts/PingFang.ttc', size=15)
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
y = [1, 15, 3, 6, 23]
plt.figure()
plt.title(u'绘制中文标题', fontproperties=getChineseFont())
plt.ylabel(u'Y轴label', fontproperties=getChineseFont())
plt.ylim(0, 30)
plt.yticks(range(0, 30, 5))
plt.plot(range(0, 5), y, "r:o", label="折线图label")
plt.show()下图中红色的即是画出来的折线图效果
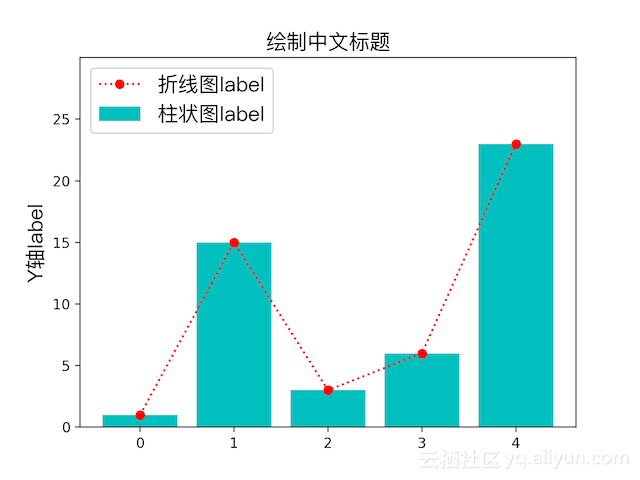
柱状图
只要将上个示例中的plot换成plt.scatter(range(0, 5), y, color='m', label="散点图label")即可画出柱状图,即上图中蓝绿色的柱子。
条状图
plot换成plt.barh(range(0, 5), y, color='y', label="条形图label")
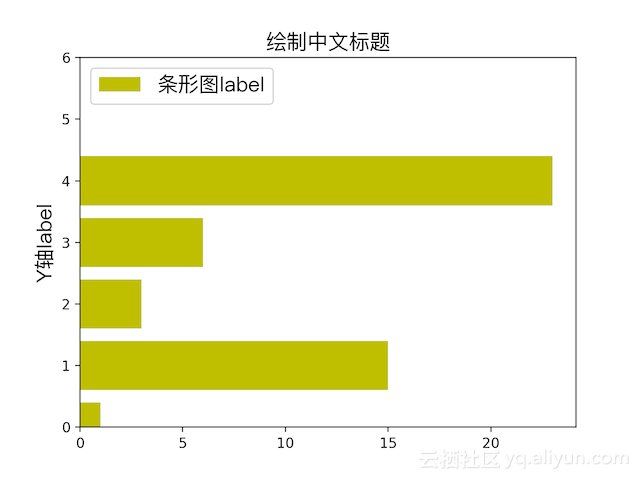
散点图
plot换成plt.scatter(range(0, 5), y, color='m', label="散点图label")
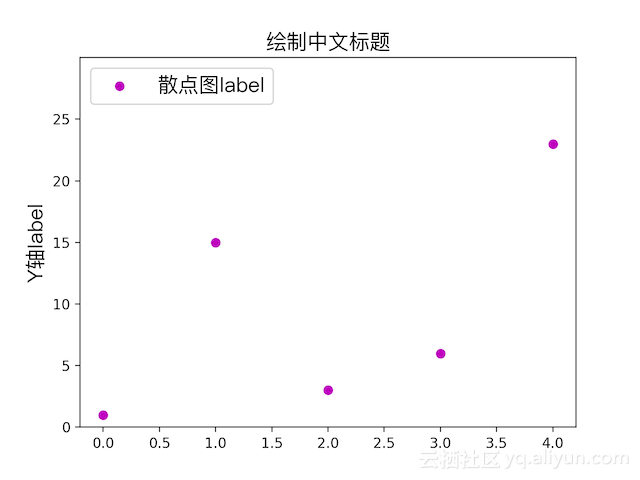
饼状图
list = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
plt.pie(list)
plt.show()
最简单的如上,给个数组即可,一般指定其他参数以使得图像更可读,下面这个还用上面的list。
labels = [u'First', 'Second', 'Third', 'Fourth'] //每块饼的标签文本
colors = ['red', 'Yellow', 'blue', 'green'] //每块饼的颜色
explode = (0.15, 0, 0, 0) //每块饼突出图形的比例
plt.pie(list, explode=explode, labels=labels
, colors=colors, startangle=60 //startangle 第一块开始的角度
, labeldistance=1.1 //标签文本距离圆心的半径比例
, pctdistance=0.6 //百分比文本距离圆心的半径比例
, autopct='%.1f%%') //百分比的格式化形式
plt.axis('equal') //x、y轴坐标系相等,这样画出来整体就是圆形
plt.legend() //需要图例
plt.show()
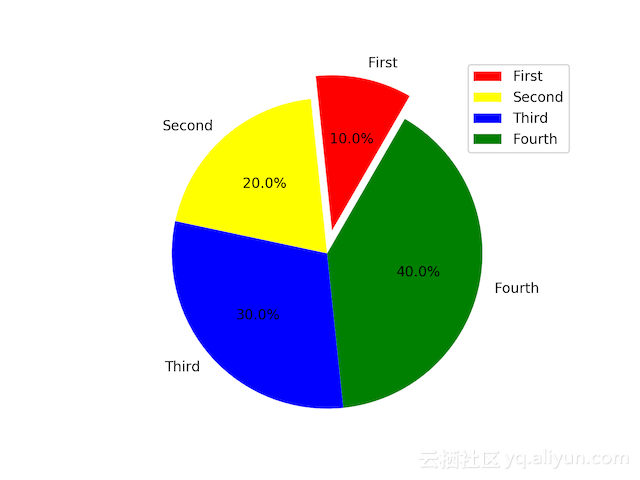
等高线图
来自 https://matplotlib.org/examples/images_contours_and_fields/contourf_log.html
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy import ma
from matplotlib import colors, ticker, cm
from matplotlib.mlab import bivariate_normal
N = 100
x = np.linspace(-3.0, 3.0, N)
y = np.linspace(-2.0, 2.0, N)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
z = (bivariate_normal(X, Y, 0.1, 0.2, 1.0, 1.0)
+ 0.1 * bivariate_normal(X, Y, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0))
z[:5, :5] = -1
z = ma.masked_where(z <= 0, z)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
cs = ax.contourf(X, Y, z, locator=ticker.LogLocator(), cmap=cm.PuBu_r)
cbar = fig.colorbar(cs)
plt.show()
灰度图、热力图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
X = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
ax.imshow(X, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
y = x
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
result = np.sqrt(X ** 2 + Y ** 2)
ax = fig.add_subplot(122)
ax.imshow(result)
plt.show()
极轴图
来自https://matplotlib.org/examples/pie_and_polar_charts/polar_bar_demo.html
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Compute pie slices
N = 20
theta = np.linspace(0.0, 2 * np.pi, N, endpoint=False)
radii = 10 * np.random.rand(N)
width = np.pi / 4 * np.random.rand(N)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection='polar')
bars = ax.bar(theta, radii, width=width, bottom=0.0)
# Use custom colors and opacity
for r, bar in zip(radii, bars):
bar.set_facecolor(plt.cm.viridis(r / 10.))
bar.set_alpha(0.5)
plt.show()
动态图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(6)
y = np.arange(5)
z = x * y[:, np.newaxis]
for i in range(5):
if i == 0:
p = plt.imshow(z)
fig = plt.gcf()
plt.clim() # clamp the color limits
plt.title("Boring slide show")
else:
z = z + 2
p.set_data(z)
print("step", i)
plt.pause(0.5)
通过每隔0.5s动态更新形成动画3D图
来自https://matplotlib.org/examples/mplot3d/surface3d_demo.html
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X ** 2 + Y ** 2)
Z = np.sin(R)
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.02f'))
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()
3D图还可以拖动用不同角度观看,实际上matplot能支持的图形还远不止这些,可以参考底部官方文档的参考。
一些有趣示例
自定义坐标系画三角函数
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 在(−π,π)之间分成共256个点,
X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256, endpoint=True)
(C, S) = np.cos(X), np.sin(X)
fig = plt.figure()
plt.plot(X, C, 'b-', lw=2.5, label='cos')
plt.plot(X, S, 'r-', lw=1.5, label='sin')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylim(C.min() * 1.2, C.max() * 1.2)
plt.xlim(X.min() * 1.2, X.max() * 1.2)
# plt.xticks([-np.pi, -np.pi / 2, 0, np.pi / 2, np.pi])
# 使用LaTeX设置更易理解的标记,即数学符号π
plt.xticks([-np.pi, -np.pi / 2, 0, np.pi / 2, np.pi],
[r'$-\pi$', r'$-\pi/2$', r'$0$', r'$\pi/2$', r'$+\pi$'])
plt.yticks([-1, 0, 1])
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') # 把右边和上边的边界设置为不可见
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0)) # 把下边界和左边界移动到0点
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
# 给特殊点添加注释
t = 2 * np.pi / 3
plt.plot([t, t], [0, np.cos(t)], color='blue', linewidth=1.0, linestyle="--")
plt.scatter([t, ], [np.cos(t), ], 50, color='blue') # 画出需要标注的点
plt.annotate(r'$\cos(\frac{2\pi}{3})=-\frac{1}{2}$',
xy=(t, np.cos(t)), xycoords='data',
xytext=(-90, -50), textcoords='offset points', fontsize=16,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3,rad=.2"))
plt.plot([t, t], [0, np.sin(t)], color='red', linewidth=1.0, linestyle="--")
plt.scatter([t, ], [np.sin(t), ], 50, color='red')
plt.annotate(r'$\sin(\frac{2\pi}{3})=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$',
xy=(t, np.sin(t)), xycoords='data',
xytext=(+10, +30), textcoords='offset points', fontsize=16,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3,rad=.2"))
# for label in ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels():
# label.set_fontsize(16)
# label.set_bbox(dict(facecolor='w', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.4))
plt.show()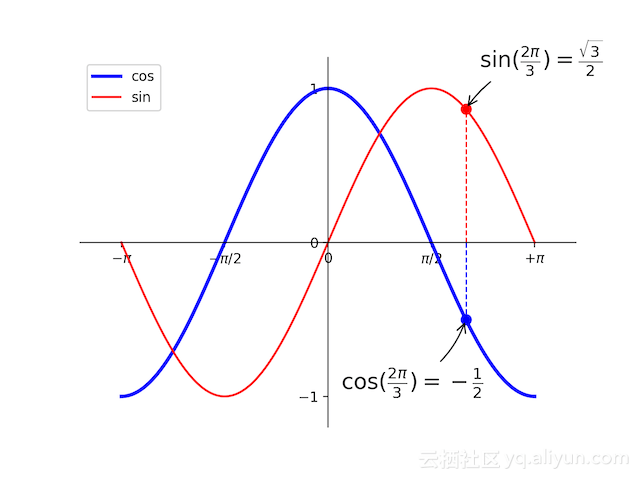
numpy里画的正态分布图
# Build a vector of 10000 normal deviates with variance 0.5^2 and mean 2
mu, sigma = 2, 0.5
v = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 5000)
# Plot a normalized histogram with 50 bins
plt.hist(v, bins=50, normed=1) # matplotlib version (plot)
# Compute the histogram with numpy and then plot it
(n, bins) = np.histogram(v, bins=50, normed=True) # NumPy version (no plot)
plt.plot(.5 * (bins[1:] + bins[:-1]), n)
plt.show()
# 简化版 http://blog.csdn.net/lanchunhui/article/details/50163669
loc = 10.0
scale = 1.0
data = np.random.normal(loc, scale, size=6000)
x_data = np.linspace(data.min(), data.max())
plt.plot(x_data, 1. / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * scale) * np.exp(-(x_data - loc) ** 2 / (2 * scale ** 2)))
count, bins, _ = plt.hist(data, 30, normed=True)
plt.show()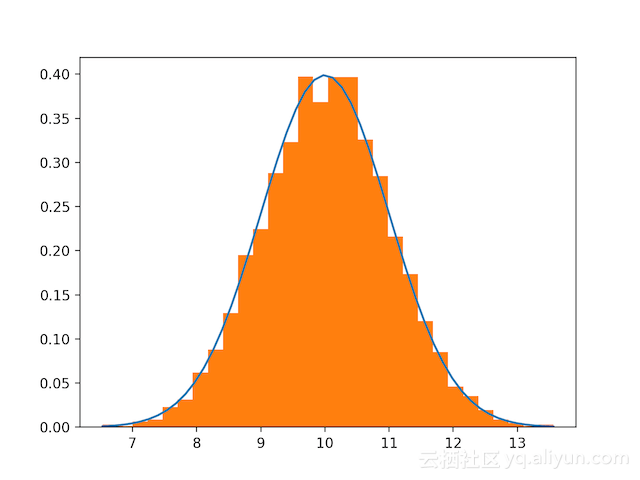
除此之外,还可以画子图其他各种形式的图,还有大量api可供使用,画出更绚丽的图片来,可看参考里的官方文档尝试。
参考
http://qianhk.com/2018/03/客户端码农学习ML-Matplotlib基本用法/
https://matplotlib.org/gallery.html
https://matplotlib.org/examples/pylab_examples/mathtext_examples.html
https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-dev/user/quickstart.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/7fbecf5255f0
https://liam0205.me/2014/09/11/matplotlib-tutorial-zh-cn/
http://conanwhf.github.io/2018/02/12/DrawByMatplotlib/
本文首发于钱凯凯的博客



