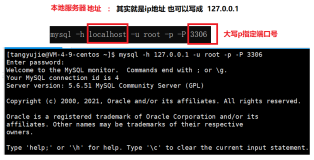
SQL> create table t as select * from dba_objects; 数据字典
SQL> desc t;
SQL> select owner from t where rownum <=10; 伪列 rowid
SQL> select count(*) from t;
伪列 rowid,rownum
SQL> delete from t where rownum<=10000;(删除t表10000行)
SQL> select OBJECT_NAME,OBJECT_ID from t order by OBJECT_ID desc(倒序)
SQL> select * from t order by OBJECT_ID asc (正序)
SQL> select count(*),owner from t group by owner;(分组)
where group by having
SQL> update t set owner='abc' where OBJECT_ID=51073;
运算符:
等于 =
大于 >
小于 <
大于等于 >=
小于等于 <=
不等于 !=
不等于 ^=
不等于 <>
---------------------
模糊查询like
( _代表一个字符,%代表所有字符)
SQL> select OBJECT_NAME,owner from t where owner like '___TT';
SQL> select * from t where owner like '%TT%';
-----------------------
is null(空) is not null (非空)
SQL> select * from t where owner is null;
------------------------
SQL> select * from t where OBJECT_ID between 51070 and 51080;
(OBJECT_ID值在10000到20000之间)
--------------------------vfast_jiaoxue_database_10
where 子查询
SQL> select * from t where owner =(select owner from t where OBJECT_ID=51079);
------------------------
组合表
create table t1 (id int,xingming varchar2(10));
insert into t1 values(1,'zs');
insert into t1 values(2,'ls');
insert into t1 values(3,'ww');
SQL> commit;
create table t2 (id int,gongzi int);
insert into t2 values(1,10000);
insert into t2 values(2,20000);
commit;
SQL> select T1.xingming,T2.gongzi from t1,t2 where T1.id=T2.id;
-------------------------
创建视图
SQL> create view v_t2
as select * from t2 where gongzi<=10000;
SQL> select * from v_t2;
---------------------------
oracle 串函数 ************
|| 连接符
SQL> select id||' '||xingming from t1;
LTRIM,RTRIM,TRIM
LTRIM:左删除
RTRIM:右删除
TRIM:删除串两边的字符
SQL> select RTRIM(gongzi,'0') from t2;
SQL> select rtrim(' aaa ') from dual;
(发现aaa的右面空格没有了)
SQL> select trim(' aaa ') from dual;
(发现aaa两端的空格没了)
---------------------------------
length求得是字符长度
SQL> select length('haha.hehe') from dual;
lengthb求得是字节长度(如有中文时使用)
SQL> select lengthb('haha.hehe') from dual;
-----------------------------------
TO_CHAR 是把日期或数字转换为字符串 ********************
SQL> select to_char(123,'9999.00') from dual
SQL> select to_char(123,'$99,999.99') from dual;
查看时间
SQL> select sysdate from dual;
SQL> select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') from dual;
SQL> create table t12 (id int,t date);
SQL> insert into t12 values(1,to_date('2012-12-12 12:12:12','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'));
--------------------------------------
substr 截取函数 ********************
SQL> select substr('abcdef',2,3) from dual;
(截取从第二个字符开始的3个字符)
SQL> select substr('abcdef',-5) from dual;
(截取后5位)
to_char(sj,'yyyy-mm-dd') t3 sj index
-------------------------------------
语法:
instr(string,substring,position,occurrence)
string:代表源字符串
substring:代表想从源字符串中查找的子串
position:代表查找开始的位置,默认为1
occurrence:代表查找值弟几次出现,结果为字符串的位置
SQL> select instr('hello word','o',-1,1) from dual;
-------------------------------------
ascii函数将字符转换成其对应的ascii码,而chr函数将数字转换成对应acscii码的字符
SQL> select ascii('a') from dual;
SQL> select chr(97) from dual;
---------------------------------------
四个字符组成的代码 (SOUNDEX) 以评估两个字符串的相似性
SQL> select soundex('two'),soundex('too'),soundex('to') from dual;
SQL> select soundex('abc'),soundex('cba') from dual;
-----------------------------------------
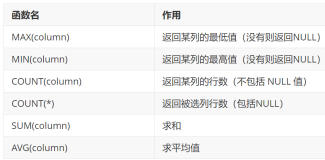
聚集函数 *************************
avg(平均值)
SQL> select avg(gongzi) from t2;
sum(求和)
SQL> select sum(gongzi) from t2;
min(最小值)
SQL> select min(gongzi) from t2;
max(最大值)
SQL> select max(gongzi) from t2;
count(行计数)
SQL> select count(*) from t2;
--------------------------------------------
nvl(返回一个非空值) ******************
nvl(e1,e2)功能为: 如果e1值为空,结果就显示为 e2设置的值
SQL> select nvl(name,0) from aa;
NVL2(E1, E2, E3)的功能为:如果E1为NULL,则函数返回E3,若E1不为null,则返回E2
SQL> select nvl2(name,1,0) from aa;
--------------------------------------------
abs ceil 返回绝对值
SQL> select abs(-5) from dual; (返回值为5)
SQL> select abs(5.5) from dual;(返回值为5.5)
SQL> select ceil(5.4) from dual;(返回值为6)
---------------------------------------------
vm_concat合并列
SQL> select * from tt;
BMID NAME GZ
---------- ---------- ----------
1 zs 10000
1 ls 12000
1 ww 15000
2 haha 30000
3 hehe 50000
显示每部门人名
SQL> select id,wm_concat(xingming) from t5 group by id;
显示每部门人名和工资
SQL> select id,wm_concat(xingming||'('||gongzi||')') from t5 group by id;
------------------------------------------
sqrt 求平方根
SQL> select sqrt(64) from dual;
--------------------------------------------
LPAD
lpad函数将左边的字符串填充一些特定的字符,其语法格式如下: lpad( String, 截取长度, 填充字符串 ) 如果截取长度比原字符串的长度要短,lpad函数将会把字符串截取成截取长度; 填充字符串是要添加到String的左边,如果这个参数未写,lpad函数将会在string1的左边补齐空格。
例如: lpad('tech', 7); 将返回' tech'
lpad('tech', 2); 将返回'te'
lpad('tech', 8, '0'); 将返回'0000tech'
lpad('tech on the net', 15, 'z'); 将返回 'tech on the net'
lpad('tech on the net', 16, 'z'); 将返回 'ztech on the net'
Lpad(str1,number,str2),这个函数的意思是,如果str1不足number那么多位,则使用str2去补齐左边的空
SELECT lpad('!!',5,'aaaa') FROM dual
--结果
aaa!!
rpad函数与lpad函数正好相反,rpad函数将左边的字符串填充一些特定的字符,其语法格式如下: rpad( String, 截取长度, 填充字符串 )
SELECT rpad('!!',5,'aaaa') FROM dual
--结果
!!aaa
------------------------------------------
Round 函数 (四舍五入) ********************
SQL> select round(123.123) from dual;
SQL> select round(123.8) from dual;
trunc 截掉小数点后值
SQL> select trunc(123.8) from dual;
-----------------------------------------------
sign取数字n的符号,大于0返回1,小于0返回-1,等于0返回0
SQL> select sign(100),sign(-100),sign(0) from dual;
-------------------------------------------------
删除重复行 ******************
SQL> select distinct(xingming) from t11;
-----------------
时间格式
SQL> select to_char(CREATED,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') from t where rownum<10;
SQL> create table tt2(id int,time date);
SQL> insert into tt2 values (1,to_date('2011-11-11 11:11:11' 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'));
SQL> select to_char(TIME,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS') from tt2;
本文转自陈继松 51CTO博客,原文链接:http://blog.51cto.com/chenjisong/1737377,如需转载请自行联系原作者