Servlet
标签 : Java与Web
会话跟踪
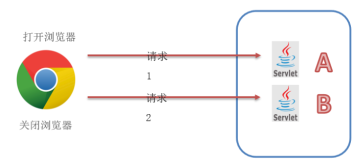
HTTP本身是“无状态”协议,它不保存连接交互信息,一次响应完成之后即连接断开,下一次请求需要重新建立连接,服务器不记录上次连接的内容.因此如果判断两次连接是否是同一用户, 就需要使用会话跟踪技术来解决.常见的会话跟踪技术有如下几种:
- URL重写: 在URL结尾附加会话ID标识,服务器通过会话ID识别不同用户.
- 隐藏表单域: 将会话ID埋入HTML表单隐藏域提交到服务端(会话ID不在浏览器页面显示).
- Cookie: 第一次请求时服务器主动发一小段信息给浏览器(即Cookie),下次请求时浏览器自动附带该段信息发送给服务器,服务器读取Cookie识别用户.
- Session: 服务器为每个用户创建一个Session对象保存到内存,并生成一个sessionID放入Cookie发送给浏览器,下次访问时sessionID会随Cookie传回来,服务器再根据sessionID找到对应Session对象(Java领域特有).
Session机制依赖于Cookie,如果Cookie被禁用Session也将失效.
Cookie
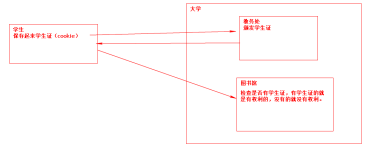
Cookie是识别当前用户,实现持久会话的最好方式.最初由网景公司开发,但现在所有主流浏览器都支持.以至于HTTP协议为他定义了一些新的HTTP首部.
URL重写与隐藏表单域两种技术都有一定的局限,细节可参考博客四种会话跟踪技术
- Cookie规范
- Cookie通过请求头/响应头在服务器与客户端之间传输, 大小限制为4KB;
- 一台服务器在一个客户端最多保存20个Cookie;
- 一个浏览器最多保存300个Cookie;
Cookie的key/value均不能保存中文,如果需要,可以在保存前对中文进行编码, 取出时再对其解码.
Java-Cookie
在Java中使用Cookie, 必须熟悉javax.servlet.http.Cookie类, 以及HttpServletRequest/HttpServletResponse接口提供的几个方法:
| Cookie | 描述 |
|---|---|
Cookie(String name, String value) |
Constructs a cookie with the specified name and value. |
String getName() |
Returns the name of the cookie. |
String getValue() |
Gets the current value of this Cookie. |
void setValue(String newValue) |
Assigns a new value to this Cookie. |
void setMaxAge(int expiry) |
Sets the maximum age in seconds for this Cookie. |
int getMaxAge() |
Gets the maximum age in seconds of this Cookie. |
void setPath(String uri) |
Specifies a path for the cookie to which the client should return the cookie. |
void setDomain(String domain) |
Specifies the domain within which this cookie should be presented. |
| Request | 描述 |
|---|---|
Cookie[] getCookies() |
Returns an array containing all of the Cookie objects the client sent with this request. |
| Response | 描述 |
|---|---|
void addCookie(Cookie cookie) |
Adds the specified cookie to the response. |
- 示例: 获取上次访问时间
从Request中获取Cookie: last_access_time, 如果没有则新建,否则显示last_access_time内容, 并更新为当前系统时间, 最后放入Response:
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
Cookie latCookie = null;
if (cookies != null){
for (Cookie cookie : cookies){
if (cookie.getName().equals(L_A_T)){
latCookie = cookie;
break;
}
}
}
// 已经访问过了
if (latCookie != null){
printResponse("您上次访问的时间是" + latCookie.getValue(), response);
latCookie.setValue(new Date().toString());
} else{
printResponse("您还是第一次访问", response);
latCookie = new Cookie(L_A_T, new Date().toString());
}
response.addCookie(latCookie);
}
private void printResponse(String data, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().print("<H1>" + data + "</H1>");
}有效期
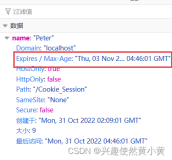
Cookie的Max-Age决定了Cookie的有效期,单位为秒.Cookie类通过getMaxAge()与setMaxAge(int maxAge)方法来读写Max-Age属性:
| Max-Age | 描述 |
|---|---|
0 |
Cookie立即作废(如果原先浏览器已经保存了该Cookie,那么可以通过设置Max-Age为0使其失效) |
< 0 |
默认,表示只在浏览器内存中存活,一旦浏览器关闭则Cookie销毁 |
> 0 |
将Cookie持久化到硬盘上,有效期由Max-Age决定 |
域属性
服务器可向Set-Cookie响应首部添加一个Domain属性来控制哪些站点可以看到该Cookie, 如
Set-Cookie: last_access_time="xxx"; Domain=.fq.com该响应首部就是在告诉浏览器将Cookie last_access_time="xxx"发送给域”.fq.com”中的所有站点(如www.fq.com, mail.fq.com).
Cookie类通过setDomain()方法设置域属性.
如果没有指定域, 则Domain默认为产生Set-Cookie响应的服务器主机名.
路径属性
Cookie规范允许用户将Cookie与部分Web站点关联起来.该功能可通过向Set-Cookie响应首部添加Path属性来实现:
Set-Cookie:last_access_time="Tue Apr 26 19:35:16 CST 2016"; Path=/servlet/这样如果访问http://www.example.com/hello_http_servlet.do就不会获得last_access_time,但如果访问http://www.example.com/servlet/index.html, 就会带上这个Cookie.
Cookie类中通过setPath()方法设置路径属性.
如果没有指定路径, Path默认为产生Set-Cookie响应的URL的路径.
Session
在所有的会话跟踪技术中, Session是功能最强大,最多的. 每个用户可以没有或者有一个HttpSession对象, 并且只能访问他自己的Session对象.
与URL重写, 隐藏表单域和Cookie不同, Session是保存在服务器内存中的数据,在达到一定的阈值后, Servlet容器会将Session持久化到辅助存储器中, 因此最好将使保存到Session内的对象实现
java.io.Serializable接口.
使用Session, 必须熟悉javax.servlet.http.HttpSession接口, 以及HttpServletRequest接口中提供的几个方法:
| HttpSession | 描述 |
|---|---|
void setAttribute(String name, Object value) |
Binds an object to this session, using the name specified. |
Object getAttribute(String name) |
Returns the object bound with the specified name in this session, or null if no object is bound under the name. |
void invalidate() |
Invalidates this session then unbinds any objects bound to it. |
Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames() |
Returns an Enumeration of String objects containing the names of all the objects bound to this session. |
void removeAttribute(String name) |
Removes the object bound with the specified name from this session. |
String getId() |
Returns a string containing the unique identifier assigned to this session. |
boolean isNew() |
Returns true if the client does not yet know about the session or if the client chooses not to join the session. |
| Request | 描述 |
|---|---|
HttpSession getSession() |
Returns the current session associated with this request, or if the request does not have a session, creates one. |
HttpSession getSession(boolean create) |
Returns the current HttpSession associated with this request or, if there is no current session and create is true, returns a new session. |
String getRequestedSessionId() |
Returns the session ID specified by the client. |
示例-购物车
- domain
/**
* @author jifang.
* @since 2016/5/1 20:14.
*/
public class Product implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String description;
private double price;
public Product(int id, String name, String description, double price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.price = price;
}
// ...
}public class ShoppingItem implements Serializable {
private Product product;
private int quantity;
public ShoppingItem(Product product, int quantity) {
this.product = product;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
// ...
}- 商品列表页面(/jsp/products.jsp)
<%@ page import="com.fq.web.domain.Product" %>
<%@ page import="com.fq.web.util.ProductContainer" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Products</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Products</h2>
<ul>
<%
for (Product product : ProductContainer.products) {
%>
<li><%=product.getName()%>
($<%=product.getPrice()%>)
(<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/jsp/product_details.jsp?id=<%=product.getId()%>">Details</a>)
</li>
<%
}
%>
</ul>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/jsp/shopping_cart.jsp">Shopping Cart</a>
</body>
</html>- 商品详情(/jsp/product_details.jsp)
<%@ page import="com.fq.web.domain.Product" %>
<%@ page import="com.fq.web.util.ProductContainer" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Product Details</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Product Details</h2>
<%
int id = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
Product product = ProductContainer.getProduct(id);
assert product != null;
%>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/session/add_to_card.do" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<%=id%>"/>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Name:</td>
<td><%=product.getName()%>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Price:</td>
<td><%=product.getPrice()%>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Description:</td>
<td><%=product.getDescription()%>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="text" name="quantity"></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Buy"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/jsp/products.jsp">Products</a></td>
<td><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/jsp/shopping_cart.jsp">Shopping Cart</a></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>- 加入购物车(AddCardServlet)
@WebServlet(name = "AddCardServlet", urlPatterns = "/session/add_to_card.do")
public class AddCardServlet extends HttpServlet {
@SuppressWarnings("All")
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
int id = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
Product product = ProductContainer.getProduct(id);
int quantity = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("quantity"));
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
List<ShoppingItem> items = (List<ShoppingItem>) session.getAttribute(SessionConstant.CART_ATTRIBUTE);
if (items == null) {
items = new ArrayList<ShoppingItem>();
session.setAttribute(SessionConstant.CART_ATTRIBUTE, items);
}
items.add(new ShoppingItem(product, quantity));
request.getRequestDispatcher("/jsp/products.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
}- 购物车(/jsp/shopping_card.jsp)
<%@ page import="com.fq.web.constant.SessionConstant" %>
<%@ page import="com.fq.web.domain.ShoppingItem" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Shopping Cart</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Shopping Cart</h2>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/jsp/products.jsp">Products</a>
<table>
<tr>
<td style="width: 150px">Quantity</td>
<td style="width: 150px">Product</td>
<td style="width: 150px">Price</td>
<td>Amount</td>
</tr>
<%
List<ShoppingItem> items = (List<ShoppingItem>) session.getAttribute(SessionConstant.CART_ATTRIBUTE);
if (items != null) {
double total = 0.0;
for (ShoppingItem item : items) {
double subtotal = item.getQuantity() * item.getProduct().getPrice();
%>
<tr>
<td><%=item.getQuantity()%>
</td>
<td><%=item.getProduct().getName()%>
</td>
<td><%=item.getProduct().getPrice()%>
</td>
<td><%=subtotal%>
</td>
</tr>
<%
total += subtotal;
}%>
<tr>
<td>Total: <%=total%>
</td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
</body>
</html>有效期
Session有一定的过期时间: 当用户长时间不去访问该Session,就会超时失效,虽然此时sessionID可能还在Cookie中, 只是服务器根据该sessionID已经找不到Session对象了.
Session的超时时间可以在web.xml中配置, 单位为分钟:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>另外一种情况: 由于sessionID保存在Cookie中且Max-Age为-1,因此当用户重新打开浏览器时已经没有sessionID了, 此时服务器会再创建一个Session,此时新的会话又开始了.而原先的Session会因为超时时间到达而被销毁.
字符编码
字符编码就是以二进制的数字来对应字符集的字符,常见字符编码方式有:ISO-8859-1(不支持中文),GB2312,GBK,UTF-8等.在JavaWeb中, 经常遇到的需要编码/解码的场景有响应编码/请求编码/URL编码:
响应编码
服务器发送数据给客户端由Response对象完成,如果响应数据是二进制流,就无需考虑编码问题.如果响应数据为字符流,那么就一定要考虑编码问题:
response.getWriter()默认使用ISO-889-1发送数据,而该字符集不支持中文,因此遇到中文就一定会乱码.
在需要发送中文时, 需要使用:
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// getWriter() ...设置编码方式,由于在getWriter()输出前已经设置了UTF-8编码,因此输出字符均为UTF-8编码,但我们并未告诉客户端使用什么编码来读取响应数据,因此我们需要在响应头中设置编码信息(使用Content-Type):
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
// getWriter() ...注意: 这句代码不只在响应头中添加了编码信息,还相当于调用了一次
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
请求编码
1. 浏览器地址栏编码
在浏览器地址栏书写字符数据,由浏览器编码后发送给服务器,因此如果在地址栏输入中文,则其编码方式由浏览器决定:
| 浏览器 | 编码 |
|---|---|
| IE/FireFox | GB2312 |
| Chrome | UTF-8 |
2. 页面请求
如果通过页面的超链接/表单向服务器发送数据,那么其编码方式由当前页面的编码方式确定:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">3. GET
当客户端发送GET请求时,无论客户端发送的数据编码方式为何,服务端均已ISO-8859-1解码(Tomcat8.x之后改用UTF-8),这就需要我们在request.getParameter()获取数据后再转换成正确的编码:
private Map<String, String> convertToParameterMap(HttpServletRequest request) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
Enumeration<String> names = request.getParameterNames();
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>();
if (names != null) {
while (names.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = names.nextElement();
String value = request.getParameter(name);
parameters.put(name, new String(value.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "UTF-8"));
}
}
return parameters;
}4. POST
当客户端发送POST请求时,服务端也是默认使用IOS-8859-1解码,但POST的数据是通过请求体传送过来,因此POST请求可以通过request.setCharacterEncoding()来指定请求体编码方式:
private Map<String, String> convertToParameterMap(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>();
if (request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
Enumeration<String> names = request.getParameterNames();
while (names.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = names.nextElement();
parameters.put(key, request.getParameter(key));
}
} else {
Enumeration<String> names = request.getParameterNames();
while (names.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = names.nextElement();
String value = request.getParameter(key);
parameters.put(key, new String(value.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "UTF-8"));
}
}
return parameters;
}URL编码
网络标准RFC 1738规定:
“…Only alphanumerics
[0-9a-zA-Z], the special characters"$-_.+!*'(),"[not including the quotes - ed], and reserved characters used for their reserved purposes may be used unencoded within a URL.”
“只有字母和数字[0-9a-zA-Z]、一些特殊符号"$-_.+!*'(),"[不包括双引号]、以及某些保留字,才可以不经过编码直接用于URL。”
如果URL中有汉字,就必须编码后使用, 而URL编码过程其实很简单:
首先需要指定一种字符编码,把字符串解码后得到
byte[],然后把小于0的字节+256,再将其转换成16进制,最后前面再添加一个%.
这个编码过程在Java中已经封装成了现成的库, 可直接使用:
| URLEncoder | 描述 |
|---|---|
static String encode(String s, String enc) |
Translates a string into application/x-www-form-urlencoded format using a specific encoding scheme. |
| URLDecoder | 描述 |
|---|---|
static String decode(String s, String enc) |
Decodes a application/x-www-form-urlencoded string using a specific encoding scheme. |
注: 在Web中Tomcat容器会自动识别URL是否已经编码并自动解码.
参考
更多有关编码知识, 可以参考:
1. 阮一峰: 关于URL编码
2. Web开发者应知的URL编码知识
3. 字符集和字符编码(Charset & Encoding)