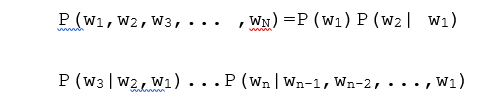最近有点累,让这篇又姗姗来迟了,各位不好意思,让你们久等了。趁着周末一个人没什么事,继续Lucene5系列的脚步,今天主题是Suggest模块下另一个功能:拼写纠错。什么叫拼写纠错?大家还是看图吧,这样会比较形象:

看完上面两张图片,我想大家应该已经知道SpellCheck是用来解决问题的了吧。其实这个功能主要目的还是为了提升用户体验问题,当用户输入的搜索关键字里包含了错别字(对于英文来说,就是单词拼写不正确),我们的搜索程序能智能检测出来并给出与用户输入的搜索关键字最相似的一组建议关键字,不过Google和百度都选择了只返回匹配度最高的一个搜索建议关键字并没有返回多个。
知道了SpellCheck是干什么的,那接下来我们需要了解SpellCheck内部是如何工作的。首先我们需要对SpellCheck有个整体的宏观的了解,所以首先还是先查阅下SpellCheck的API文档:

API里对于SpellChecker类没有太多说明,只是说这个SpellCheck功能的主类,代码作者是xxxxxx谁,这些信息对于我们来说没什么太大的价值,后面给出了一个使用示例,我们暂时也不急怎么去使用它,我们学习一个新的类或接口,我们首先需要理解它内部有哪些成员变量以及定义了哪些方法,以及每个方法的含义,这些API里都有说明,看图:

定义了两个publick公开的静态成员变量,DEFAULT_ACCURACY表示默认的最小分数,SpellCheck会对字典里的每个词与用户输入的搜索关键字进行一个相似度打分,默认该值是0.5,相似度分值范围是0到1之间,数字越大表示越相似。F_WORD是对于字典文件里每一行创建索引时使用的默认域名称,默认值为:word
然后看看有哪些方法并了解每个方法的用途:

clearIndex: 移除拼写检查索引中的所有Term项;
close: 关闭IndexSearcher的reader;
exist:判断用户输入的关键字是否存在于拼写检查索引中
getAccuracy:accuracy是精确度的意思,这里表示最小评分,评分越大表示与用户输入的关键字越相似
suggestSimilar:这个方法就是用来决定哪些word会被判定为比较相似的然后以数组的形式返回,这是SpellChecker的核心;
setComparator:设置比较器,既然涉及到相似度问题,那肯定有相似度大小问题,有大小必然存在比较,有比较必然需要比较器,通过比较器决定返回的建议词的顺序,因为一般需要把最相关的显示在最前面,然后依次排序显示;
setSpellIndex:设置拼写检查索引目录的
setStringDistance:设置编辑距实现
当然内部还有一些private内置函数在API里并未体现。大概了解了SpellChecker的内部设计,如果更深入了解SpellChcker则需要通过阅读它的源码:
- <strong>/**
- * <p>
- * Spell Checker class (Main class) <br/>
- * (initially inspired by the David Spencer code).
- * </p>
- *
- * <p>Example Usage:
- *
- * <pre class="prettyprint">
- * SpellChecker spellchecker = new SpellChecker(spellIndexDirectory);
- * // To index a field of a user index:
- * spellchecker.indexDictionary(new LuceneDictionary(my_lucene_reader, a_field));
- * // To index a file containing words:
- * spellchecker.indexDictionary(new PlainTextDictionary(new File("myfile.txt")));
- * String[] suggestions = spellchecker.suggestSimilar("misspelt", 5);
- * </pre>
- *
- *
- */
- public class SpellChecker implements java.io.Closeable {
- /**
- * The default minimum score to use, if not specified by calling {@link #setAccuracy(float)} .
- */
- public static final float DEFAULT_ACCURACY = 0.5f;
- /**
- * Field name for each word in the ngram index.
- */
- public static final String F_WORD = "word";
- /**
- * the spell index
- */
- // don't modify the directory directly - see #swapSearcher()
- // TODO: why is this package private?
- Directory spellIndex;
- /**
- * Boost value for start and end grams
- */
- private float bStart = 2.0f;
- private float bEnd = 1.0f;
- // don't use this searcher directly - see #swapSearcher()
- private IndexSearcher searcher;
- /*
- * this locks all modifications to the current searcher.
- */
- private final Object searcherLock = new Object();
- /*
- * this lock synchronizes all possible modifications to the
- * current index directory. It should not be possible to try modifying
- * the same index concurrently. Note: Do not acquire the searcher lock
- * before acquiring this lock!
- */
- private final Object modifyCurrentIndexLock = new Object();
- private volatile boolean closed = false;
- // minimum score for hits generated by the spell checker query
- private float accuracy = DEFAULT_ACCURACY;
- private StringDistance sd;
- private Comparator<SuggestWord> comparator;</strong>
public static final float DEFAULT_ACCURACY = 0.5f;
这里设置了默认的相似度值,小于这个值就不会被返回了即默认会认为相似度小于0.5的就是不相似的。
public static final String F_WORD = "word";
我们在创建拼写索引时默认使用的域名称
Directory spellIndex:拼写索引目录
private float bStart = 2.0f;
private float bEnd = 1.0f;
这两个分别是前缀ngram和后缀ngram的权重值,即默认认为前缀ngram权重比后缀ngram大,ngram就是按定长来分割字符串成多个Term,比如lucene,假如采用3gram,则最后返回的Term数组为:luc,uce,cen,ene,显然这里luc是前缀ngram,ene是后缀ngram,当然你也可以采用2gram,只不过这时返回的term个数更多,Term个数多自然查询更精确,但响应速度也会慢些。如果ngram这里的N取值大的话,那匹配粒度大,虽然查询精确度会下降,但响应速度也加快了。
private IndexSearcher searcher; 索引查询器对象,这个没什么好说的;
private final Object searcherLock = new Object(); 查询锁,进行查询之间需要先占有这把锁
private final Object modifyCurrentIndexLock = new Object();
修改索引锁,在添加索引或更新索引时需要获取这把锁
private volatile boolean closed = false;
标识IndexReader是否已经关闭
private StringDistance sd;
编辑距实现
private Comparator<SuggestWord> comparator;建议词比较器,决定了最终返回的拼写建议词在SuggestWordQueue队列中的排序
setSpellIndex:
- <strong>public void setSpellIndex(Directory spellIndexDir) throws IOException {
- // this could be the same directory as the current spellIndex
- // modifications to the directory should be synchronized
- synchronized (modifyCurrentIndexLock) {
- ensureOpen();
- if (!DirectoryReader.indexExists(spellIndexDir)) {
- IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(spellIndexDir,
- new IndexWriterConfig(null));
- writer.close();
- }
- swapSearcher(spellIndexDir);
- }
- }</strong>
先拿到modifyCurrentIndexLock索引修改锁,防止索引被修改,
ensureOpen();确保索引目录能打开
DirectoryReader.indexExists(spellIndexDir):判断指定索引目录下是否存在段文件,如果不存在则关闭IndexWrtier,然后通过swapSearcher重新打开IndexReader。
- private static String[] formGrams(String text, int ng) {
- int len = text.length();
- String[] res = new String[len - ng + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < len - ng + 1; i++) {
- res[i] = text.substring(i, i + ng);
- }
- return res;
- }
formGrams:根据提供的ng长度对text字符串进行ngram分割,返回分割后得到的gram数组
- /**
- * Removes all terms from the spell check index.
- * @throws IOException If there is a low-level I/O error.
- * @throws AlreadyClosedException if the Spellchecker is already closed
- */
- public void clearIndex() throws IOException {
- synchronized (modifyCurrentIndexLock) {
- ensureOpen();
- final Directory dir = this.spellIndex;
- final IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(dir, new IndexWriterConfig(null)
- .setOpenMode(OpenMode.CREATE));
- writer.close();
- swapSearcher(dir);
- }
- }
clearIndex:首先获取修改索引锁,防止索引没修改,然后ensureOpen确保索引目录能被打开,然后重新new了一个IndexWriter且索引写入模式设置为create即先前的索引将会被覆盖,然后close掉IndexWrtier,最后打开Reader重新new一个IndexWriter.这样做是为了覆盖掉先前的索引(OpenMode.CREATE是关键),即clearIndex方法的目的。
- /**
- * Indexes the data from the given {@link Dictionary}.
- * @param dict Dictionary to index
- * @param config {@link IndexWriterConfig} to use
- * @param fullMerge whether or not the spellcheck index should be fully merged
- * @throws AlreadyClosedException if the Spellchecker is already closed
- * @throws IOException If there is a low-level I/O error.
- */
- public final void indexDictionary(Dictionary dict, IndexWriterConfig config, boolean fullMerge) throws IOException {
- synchronized (modifyCurrentIndexLock) {
- ensureOpen();
- final Directory dir = this.spellIndex;
- final IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(dir, config);
- IndexSearcher indexSearcher = obtainSearcher();
- final List<TermsEnum> termsEnums = new ArrayList<>();
- final IndexReader reader = searcher.getIndexReader();
- if (reader.maxDoc() > 0) {
- for (final LeafReaderContext ctx : reader.leaves()) {
- Terms terms = ctx.reader().terms(F_WORD);
- if (terms != null)
- termsEnums.add(terms.iterator(null));
- }
- }
- boolean isEmpty = termsEnums.isEmpty();
- try {
- BytesRefIterator iter = dict.getEntryIterator();
- BytesRef currentTerm;
- terms: while ((currentTerm = iter.next()) != null) {
- String word = currentTerm.utf8ToString();
- int len = word.length();
- if (len < 3) {
- continue; // too short we bail but "too long" is fine...
- }
- if (!isEmpty) {
- for (TermsEnum te : termsEnums) {
- if (te.seekExact(currentTerm)) {
- continue terms;
- }
- }
- }
- // ok index the word
- Document doc = createDocument(word, getMin(len), getMax(len));
- writer.addDocument(doc);
- }
- } finally {
- releaseSearcher(indexSearcher);
- }
- if (fullMerge) {
- writer.forceMerge(1);
- }
- // close writer
- writer.close();
- // TODO: this isn't that great, maybe in the future SpellChecker should take
- // IWC in its ctor / keep its writer open?
- // also re-open the spell index to see our own changes when the next suggestion
- // is fetched:
- swapSearcher(dir);
- }
- }
先通过IndexReader读取索引目录,加载word域上的所有Term存入TermEnum集合中,然后加载字典文件(字典文件里一行一个词),遍历字典文件里的每个词,内层循环里遍历索引目录里word域上的每个Term,如果当前字典文件里的词在word域中存在(避免Term重复),则直接跳过,否则需要将字典文件里当前词写入索引,这里存入索引并不是直接把当前词存入索引,这里还有个ngram过程,通过ngram分成多个Term再写入索引的,即这句代码Document doc = createDocument(word, getMin(len), getMax(len));min和max即ngram的分割长度范围。然后writer.addDocument(doc);写入索引目录,然后释放IndexReader即releaseSearcher(indexSearcher);,如果设置了fullMerge则会强制将段文件合并为一个即writer.forceMerge(1);最后关闭IndexWriter,最后swapSearcher(dir);即IndexReader重新打开,new一个新的IndexSearcher,保证新加的document被被search到。一句话总结:indexDictionary就是将字典文件里的词进行ngram操作后得到多个词然后分别写入索引。
- /**
- * Suggest similar words (optionally restricted to a field of an index).
- *
- * <p>As the Lucene similarity that is used to fetch the most relevant n-grammed terms
- * is not the same as the edit distance strategy used to calculate the best
- * matching spell-checked word from the hits that Lucene found, one usually has
- * to retrieve a couple of numSug's in order to get the true best match.
- *
- * <p>I.e. if numSug == 1, don't count on that suggestion being the best one.
- * Thus, you should set this value to <b>at least</b> 5 for a good suggestion.
- *
- * @param word the word you want a spell check done on
- * @param numSug the number of suggested words
- * @param ir the indexReader of the user index (can be null see field param)
- * @param field the field of the user index: if field is not null, the suggested
- * words are restricted to the words present in this field.
- * @param suggestMode
- * (NOTE: if indexReader==null and/or field==null, then this is overridden with SuggestMode.SUGGEST_ALWAYS)
- * @param accuracy The minimum score a suggestion must have in order to qualify for inclusion in the results
- * @throws IOException if the underlying index throws an {@link IOException}
- * @throws AlreadyClosedException if the Spellchecker is already closed
- * @return String[] the sorted list of the suggest words with these 2 criteria:
- * first criteria: the edit distance, second criteria (only if restricted mode): the popularity
- * of the suggest words in the field of the user index
- *
- */
- public String[] suggestSimilar(String word, int numSug, IndexReader ir,
- String field, SuggestMode suggestMode, float accuracy) throws IOException {
- // obtainSearcher calls ensureOpen
- final IndexSearcher indexSearcher = obtainSearcher();
- try {
- if (ir == null || field == null) {
- suggestMode = SuggestMode.SUGGEST_ALWAYS;
- }
- if (suggestMode == SuggestMode.SUGGEST_ALWAYS) {
- ir = null;
- field = null;
- }
- final int lengthWord = word.length();
- final int freq = (ir != null && field != null) ? ir.docFreq(new Term(field, word)) : 0;
- final int goalFreq = suggestMode==SuggestMode.SUGGEST_MORE_POPULAR ? freq : 0;
- // if the word exists in the real index and we don't care for word frequency, return the word itself
- if (suggestMode==SuggestMode.SUGGEST_WHEN_NOT_IN_INDEX && freq > 0) {
- return new String[] { word };
- }
- BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery();
- String[] grams;
- String key;
- for (int ng = getMin(lengthWord); ng <= getMax(lengthWord); ng++) {
- key = "gram" + ng; // form key
- grams = formGrams(word, ng); // form word into ngrams (allow dups too)
- if (grams.length == 0) {
- continue; // hmm
- }
- if (bStart > 0) { // should we boost prefixes?
- add(query, "start" + ng, grams[0], bStart); // matches start of word
- }
- if (bEnd > 0) { // should we boost suffixes
- add(query, "end" + ng, grams[grams.length - 1], bEnd); // matches end of word
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < grams.length; i++) {
- add(query, key, grams[i]);
- }
- }
- int maxHits = 10 * numSug;
- // System.out.println("Q: " + query);
- ScoreDoc[] hits = indexSearcher.search(query, null, maxHits).scoreDocs;
- // System.out.println("HITS: " + hits.length());
- SuggestWordQueue sugQueue = new SuggestWordQueue(numSug, comparator);
- // go thru more than 'maxr' matches in case the distance filter triggers
- int stop = Math.min(hits.length, maxHits);
- SuggestWord sugWord = new SuggestWord();
- for (int i = 0; i < stop; i++) {
- sugWord.string = indexSearcher.doc(hits[i].doc).get(F_WORD); // get orig word
- // don't suggest a word for itself, that would be silly
- if (sugWord.string.equals(word)) {
- continue;
- }
- // edit distance
- sugWord.score = sd.getDistance(word,sugWord.string);
- if (sugWord.score < accuracy) {
- continue;
- }
- if (ir != null && field != null) { // use the user index
- sugWord.freq = ir.docFreq(new Term(field, sugWord.string)); // freq in the index
- // don't suggest a word that is not present in the field
- if ((suggestMode==SuggestMode.SUGGEST_MORE_POPULAR && goalFreq > sugWord.freq) || sugWord.freq < 1) {
- continue;
- }
- }
- sugQueue.insertWithOverflow(sugWord);
- if (sugQueue.size() == numSug) {
- // if queue full, maintain the minScore score
- accuracy = sugQueue.top().score;
- }
- sugWord = new SuggestWord();
- }
- // convert to array string
- String[] list = new String[sugQueue.size()];
- for (int i = sugQueue.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- list[i] = sugQueue.pop().string;
- }
- return list;
- } finally {
- releaseSearcher(indexSearcher);
- }
- }
现在来说说核心函数suggestSimilar,用来计算最后返回的建议词。首先需要说下SuggestMode的建议模式:
SUGGEST_WHEN_NOT_IN_INDEX:
意思就是只有当用户提供的搜索关键字在索引Term中不存在我才提供建议,否则我会认为用户输入的搜索关键字是正确的不需要提供建议。
SUGGEST_MORE_POPULAR:
表示只返回频率较高的词组,用户输入的搜索关键字首先需要经过ngram分割,创建索引的时候也需要进行分词,如果用户输入的词分割后得到的word在索引中出现的频率比索引中实际存在的Term还要高,那说明不需要进行拼写建议了。
SUGGEST_ALWAYS:
永远进行建议,只是返回的建议结果受numSug数量限制即最多返回几条拼写建议。
if (suggestMode==SuggestMode.SUGGEST_WHEN_NOT_IN_INDEX && freq > 0) {
return new String[] { word };
}
这里freq>0表明用户输入的搜索关键字在Term中出现了且你配置只对搜索关键字在索引中不存在才进行拼写建议,则直接返回用户数的原词即默认用户输入是正确的,不需要进行拼写建议
for (int ng = getMin(lengthWord); ng <= getMax(lengthWord); ng++)
然后根据用户输入的搜索关键字的长度确定进行ngram的分割长度范围,然后对用户输入的搜索关键字进行ngram操作并把分割出的每个词使用booleanQuery链接(默认用的or链接)起来,如果是前缀ngram和后缀ngram还需要设置不同的权重,然后根据创建的Query进行检索:
ScoreDoc[] hits = indexSearcher.search(query, null, maxHits).scoreDocs;
然后遍历实际命中的结果集for (int i = 0; i < stop; i++),这里的stop即结果集的实际长度,取出每个Term与当前用户输入的关键字进行比对,如果equals则直接pass,因为需要排除自身,即这句代码:
if (sugWord.string.equals(word)) {
continue;
}
sugWord.score = sd.getDistance(word,sugWord.string);
返回用户输入关键字和索引中当前Term的相似度,这个取决于你Distance实现,默认实现是LevensteinDistance即计算编辑距。
if (sugWord.score < accuracy) {
continue;
}
如果相似度小于设置的默认值则也不返回
if ((suggestMode==SuggestMode.SUGGEST_MORE_POPULAR && goalFreq > sugWord.freq) || sugWord.freq < 1) {
continue;
}
在SUGGEST_MORE_POPULAR 模式下,如果用户输入的关键字都比索引中的Term的出现频率高,那也直接跳过不返回(用户输入的关键字出现频率高,说明该关键字匹配度高啊,通过该关键字搜索自然会有结果集返回,自然不需要进行拼写检查啊)
sugQueue.insertWithOverflow(sugWord);
if (sugQueue.size() == numSug) {
accuracy = sugQueue.top().score;
}
条件符合那就把当前索引中的Term存入拼写建议队列中,如果队列满了则把队列顶部的score(即相似度)缓存到accuracy即该值就表示了当前最小的相似度值,因为当队列满了,自然是要把相似度最小的给移除啊,处于顶部的自然是最小的,所以你懂的。
sugWord = new SuggestWord();然后把SuggestWord重置进入索引中下一个Term匹配过程如此循环。
for (int i = sugQueue.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
list[i] = sugQueue.pop().string;
}
最后把队列里的word一个个pop从队列中弹出,因为是倒着赋值的(从数组尾部赋值的),那自然最终返回的数组里相似度高的在前面,相似度低的处于数组尾部。
关键重点是sugWord.score = sd.getDistance(word,sugWord.string);
判断两个词的相似度,默认实现是LevensteinDistance,至于LevensteinDistance算法实现自己去看LevensteinDistance源码吧。
其实lucene还内置了另外几种相似度实现:JaroWinklerDistance和NGramDistance。
Distance实现可以在构造SpellChecker时通过其构造函数进行自定义,
- /**
- * Use the given directory as a spell checker index. The directory
- * is created if it doesn't exist yet.
- * @param spellIndex the spell index directory
- * @param sd the {@link StringDistance} measurement to use
- * @throws IOException if Spellchecker can not open the directory
- */
- public SpellChecker(Directory spellIndex, StringDistance sd) throws IOException {
- this(spellIndex, sd, SuggestWordQueue.DEFAULT_COMPARATOR);
- }
另外一个重点是comparator,在构造SpellChecker时如果没有显式设置comparator,则默认构造的是SuggestWordQueue.DEFAULT_COMPARATOR即SuggestWordScoreComparator,SuggestWordScoreComparator的比较规则是:
先比较socre值即相似度值(这个相似度值是有Distance类决定的),如果score值相等,则再来比较freq即索引中出现频率,频率高则相似度高,如果还是分不出高下,则直接比较两个字符串吧,字符串比较其实就是从左至右逐个字符比较他们的ASCII码。
其实Compartor比较器也是可以通过构造函数重载进行指定的,如果默认的比较器满足不了你的要求,请自定义你自己的比较器,你懂的。
还有一个重点就是Dictionary实现,它有3个实现:
1. PlainTextDictionary:即文本字典文件,即从文本文件中读取内容来构建索引,不过要求一行只能一个词,内部会对每一行的词进行ngram分割然后才写入索引中
2.LuceneDictionary:即直接以已经存在的索引中的某个域的值作为字典
3.HighFrequencyDictionary:跟LuceneDictionary类似,它跟LuceneDictionary区别就是它限制了只有出现在各document中的次数满足一定数量时才会被写入索引,这个数量通过构造函数的thresh参数决定。
Dictionary实现类通过SpellChecker的indexDictionary方法指定。
按照惯例下面还是来段示例代码吧:
- package com.yida.framework.lucene5.spellcheck;
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.nio.file.Paths;
- import org.apache.lucene.analysis.standard.StandardAnalyzer;
- import org.apache.lucene.document.Document;
- import org.apache.lucene.document.Field.Store;
- import org.apache.lucene.document.TextField;
- import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexReader;
- import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter;
- import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriterConfig;
- import org.apache.lucene.search.IndexSearcher;
- import org.apache.lucene.search.spell.PlainTextDictionary;
- import org.apache.lucene.search.spell.SpellChecker;
- import org.apache.lucene.store.Directory;
- import org.apache.lucene.store.RAMDirectory;
- /**
- * 拼写检查测试
- * @author Lanxiaowei
- *
- */
- public class SpellCheckTest {
- private static String dicpath = "C:/dictionary.dic";
- private Document document;
- private Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();
- private IndexWriter indexWriter;
- /**拼写检查器*/
- private SpellChecker spellchecker;
- private IndexReader indexReader;
- private IndexSearcher indexSearcher;
- /**
- * 创建测试索引
- * @param content
- * @throws IOException
- */
- public void createIndex(String content) throws IOException {
- IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(new StandardAnalyzer());
- indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
- document = new Document();
- document.add(new TextField("content", content,Store.YES));
- try {
- indexWriter.addDocument(document);
- indexWriter.commit();
- indexWriter.close();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- public void search(String word, int numSug) {
- directory = new RAMDirectory();
- try {
- IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(new StandardAnalyzer());
- spellchecker = new SpellChecker(directory);
- //初始化字典目录
- //最后一个fullMerge参数表示拼写检查索引是否需要全部合并
- spellchecker.indexDictionary(new PlainTextDictionary(Paths.get(dicpath)),config,true);
- //这里的参数numSug表示返回的建议个数
- String[] suggests = spellchecker.suggestSimilar(word, numSug);
- if (suggests != null && suggests.length > 0) {
- for (String suggest : suggests) {
- System.out.println("您是不是想要找:" + suggest);
- }
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- SpellCheckTest spellCheckTest = new SpellCheckTest();
- spellCheckTest.createIndex("《屌丝男士》不是传统意义上的情景喜剧,有固定时长和单一场景,以及简单的生活细节。而是一部具有鲜明网络特点,舞台感十足,整体没有剧情衔接,固定的演员演绎着并不固定角色的笑话集。");
- spellCheckTest.createIndex("屌丝男士的拍摄构想,首先源于“屌丝文化”在中国的刮起的现象级春风,红透了整片天空,全中国上下可谓无人不屌丝,无人不爱屌丝。");
- spellCheckTest.createIndex("德国的一部由女演员玛蒂娜-希尔主演的系列短剧,凭借其疯癫荒诞、自high耍贱、三俗无下限的表演风格,在中国取得了巨大成功,红火程度远远超过了德国。不仅位居国内各个视频网站的下载榜和点播榜高位,且在微博和媒体间,引发了坊间热议和话题传播。网友们更是形象地将其翻译为《屌丝女士》,对其无比热衷。于是我们决定着手拍一部属于中国人,带强烈国人屌丝色彩的《屌丝男士》。");
- String word = "吊丝男士";
- spellCheckTest.search(word, 5);
- }
- }
在C盘新建一个dictionary.dic文件,编辑内容如图:
OK,有关SpellCheck拼写纠错功能就说到这儿了,如果还有哪里不清楚的请联系我,demo源码请在最底下的附件里下载。
如果你还有什么问题请加我Q-Q:7-3-6-0-3-1-3-0-5,
或者加裙 一起交流学习!
一起交流学习!
转载:http://iamyida.iteye.com/blog/2206107