前言
Solr现在是一个独立的服务器。
从Solr5.0开始,Solr不再发布为在任何Servlet容器中部署的“war”Web应用程序包(Web Application Archive)。Solr现在部署为一个独立的java服务器应用程序,包含在Unix和Windows平台上可以使用的启动和停止脚本,以及将Solr作为服务安装到类Unix平台的/etc/init.d下的安装脚本。
本质上,Solr仍然以Servlet APIs实现,并在Jetty上运行,但只是作为一个实现。部署为“webapp”到其他的Servlet容器(或其他Jetty实例)上不被支持,可能在未来的Solr 5.x版本不会工作。而可能会带来Solr的其他改变,事实上是利用自定义网络协议栈功能。
安装JRE
-
需要Java Runtime Environment(JRE) 1.7或更高版本,先验证。
1# java -version -
安装可参考《在CentOS下安装JDK8》,包含JRE。
安装Solr5.3
-
去http://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.lua/lucene/solr/5.3.0下载Solr安装文件solr-5.3.0.tgz。
-
将solr-5.3.0.tgz文件放到/tmp目录下,执行如下脚本:
12# cd /tmp# tar -zxvf solr-5.3.0.tgz // 解压压缩包 -
创建应用程序和数据目录
1# mkdir -p /data/solr /usr/local/solr -
创建运行solr的用户并赋权
123# groupadd solr# useradd -g solr solr# chown -R solr.solr /data/solr /usr/local/solr -
安装solr服务
1# solr-5.3.0/bin/install_solr_service.sh solr-5.3.0.tgz -d /data/solr -i /usr/local/solr -
检查服务状态
1# service solr status将会看到如下输出:
1234567Solr process 29692 running on port 8983{"solr_home":"/data/solr/data/","version":"5.3.0 1696229 - noble - 2015-08-17 17:10:43","startTime":"2015-09-16T01:32:03.919Z","uptime":"0 days, 0 hours, 3 minutes, 6 seconds","memory":"89.8 MB (%18.3) of 490.7 MB"}
solr命令用法
-
定位到solr应用程序目录
1# cd /usr/local/solr/solr -
查看solr命令选项
1# ./bin/solr
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
Usage: solr COMMAND OPTIONS where COMMAND is one of: start, stop, restart, status, healthcheck, create, create_core, create_collection, delete
Standalone server example (start Solr running in the background on port 8984):
./solr start -p 8984
SolrCloud example (start Solr running in SolrCloud mode using localhost:2181 to connect to ZooKeeper, with 1g max heap size and remote Java debug options enabled):
./solr start -c -m 1g -z localhost:2181 -a "-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=1044"
Pass -help after any COMMAND to see command-specific usage information, such as: ./solr start -help or ./solr stop -help
|
|
1
|
# ./bin/solr start -help
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
Usage: solr start [-f] [-c] [-h hostname] [-p port] [-d directory] [-z zkHost] [-m memory] [-e example] [-s solr.solr.home] [-a "additional-options"] [-V]
-f Start Solr in foreground; default starts Solr in the background and sends stdout / stderr to solr-PORT-console.log
-c or -cloud Start Solr in SolrCloud mode; if -z not supplied, an embedded ZooKeeper instance is started on Solr port+1000, such as 9983 if Solr is bound to 8983
-h <host> Specify the hostname for this Solr instance
-p <port> Specify the port to start the Solr HTTP listener on; default is 8983 The specified port (SOLR_PORT) will also be used to determine the stop port STOP_PORT=($SOLR_PORT-1000) and JMX RMI listen port RMI_PORT=(1$SOLR_PORT). For instance, if you set -p 8985, then the STOP_PORT=7985 and RMI_PORT=18985
-d <dir> Specify the Solr server directory; defaults to server
-z <zkHost> ZooKeeper connection string; only used when running in SolrCloud mode using -c To launch an embedded ZooKeeper instance, don't pass this parameter.
-m <memory> Sets the min (-Xms) and max (-Xmx) heap size for the JVM, such as: -m 4g results in: -Xms4g -Xmx4g; by default, this script sets the heap size to 512m
-s <dir> Sets the solr.solr.home system property; Solr will create core directories under this directory. This allows you to run multiple Solr instances on the same host while reusing the same server directory set using the -d parameter. If set, the specified directory should contain a solr.xml file, unless solr.xml exists in ZooKeeper. This parameter is ignored when running examples (-e), as the solr.solr.home depends on which example is run. The default value is server/solr.
-e <example> Name of the example to run; available examples: cloud: SolrCloud example techproducts: Comprehensive example illustrating many of Solr's core capabilities dih: Data Import Handler schemaless: Schema-less example
-a Additional parameters to pass to the JVM when starting Solr, such as to setup Java debug options. For example, to enable a Java debugger to attach to the Solr JVM you could pass: -a "-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=18983" In most cases, you should wrap the additional parameters in double quotes.
-noprompt Don't prompt for input; accept all defaults when running examples that accept user input
-V Verbose messages from this script
|
|
1
|
# ./bin/solr create -help
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
Usage: solr create [-c name] [-d confdir] [-n configName] [-shards #] [-replicationFactor #] [-p port]
Create a core or collection depending on whether Solr is running in standalone (core) or SolrCloud mode (collection). In other words, this action detects which mode Solr is running in, and then takes the appropriate action (either create_core or create_collection). For detailed usage instructions, do:
bin/solr create_core -help
or
bin/solr create_collection –help
|
安装solr服务脚本用法
-
运行安装脚本
1# /tmp/solr-5.3.0/bin/install_solr_service.sh
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
ERROR: Must specify the path to the Solr installation archive, such as solr-5.0.0.tgz
Usage: install_solr_service.sh path_to_solr_distribution_archive OPTIONS
The first argument to the script must be a path to a Solr distribution archive, such as solr-5.0.0.tgz (only .tgz or .zip are supported formats for the archive)
Supported OPTIONS include:
-d Directory for live / writable Solr files, such as logs, pid files, and index data; defaults to /var/solr
-i Directory to extract the Solr installation archive; defaults to /opt/ The specified path must exist prior to using this script.
-p Port Solr should bind to; default is 8983
-s Service name; defaults to solr
-u User to own the Solr files and run the Solr process as; defaults to solr This script will create the specified user account if it does not exist.
NOTE: Must be run as the root user
|
创建集合
在这个部分,我们创建一个简单的Solr集合。
Solr可以有多个集合,但在这个示例,我们只使用一个。使用如下命令,创建一个新的集合。我们以solr用户运行以避免任何权限错误。
|
1
|
# su - solr -c "/usr/local/solr/solr/bin/solr create -c gettingstarted -n data_driven_schema_configs"
|
在这个命令中,gettingstarted是集合的名字,-n指定配置集合。Solr默认提供了3个配置集合。这里我们使用的是schemaless,意思是可以提供任意名字的任意列,类型将会被猜测。
|
1
2
3
|
Setup new core instance directory: /data/solr/data/gettingstarted
Creating new core 'gettingstarted' using command: http://localhost:8983/solr/admin/cores?action=CREATE&name=gettingstarted&instanceDir=gettingstarted
{ "responseHeader":{ "status":0, "QTime":3247}, "core":"gettingstarted"}
|
你现在已经创建了集合,并可以开始添加数据。默认的架构只需要提供一列:id。没有其他默认列,只有动态列。
添加和查询文档
在这个部分,我们将浏览Solr Web界面,添加一些文档到集合中。
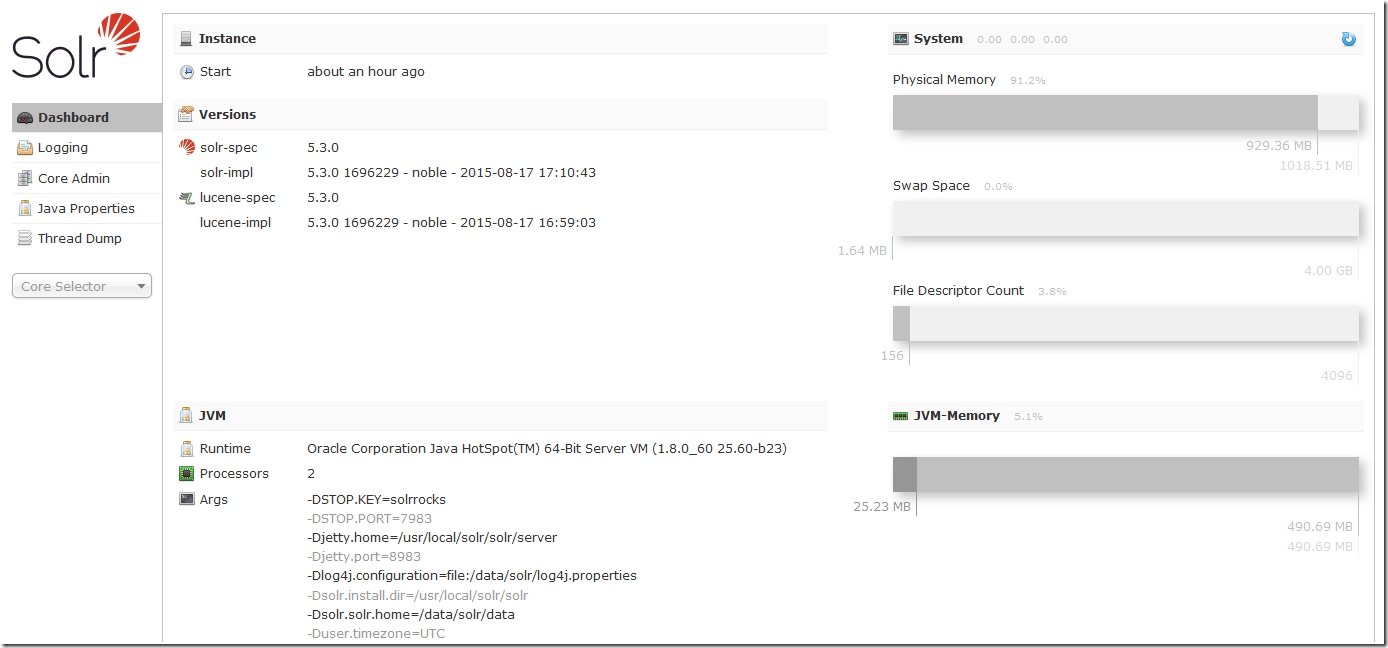
问你使用Web浏览器访问http://your_server_ip:8983/solr,Solr Web界面将会显示为:
这个Web界面包含大量的有用信息,可以被用于调试在使用中产生的任何问题。
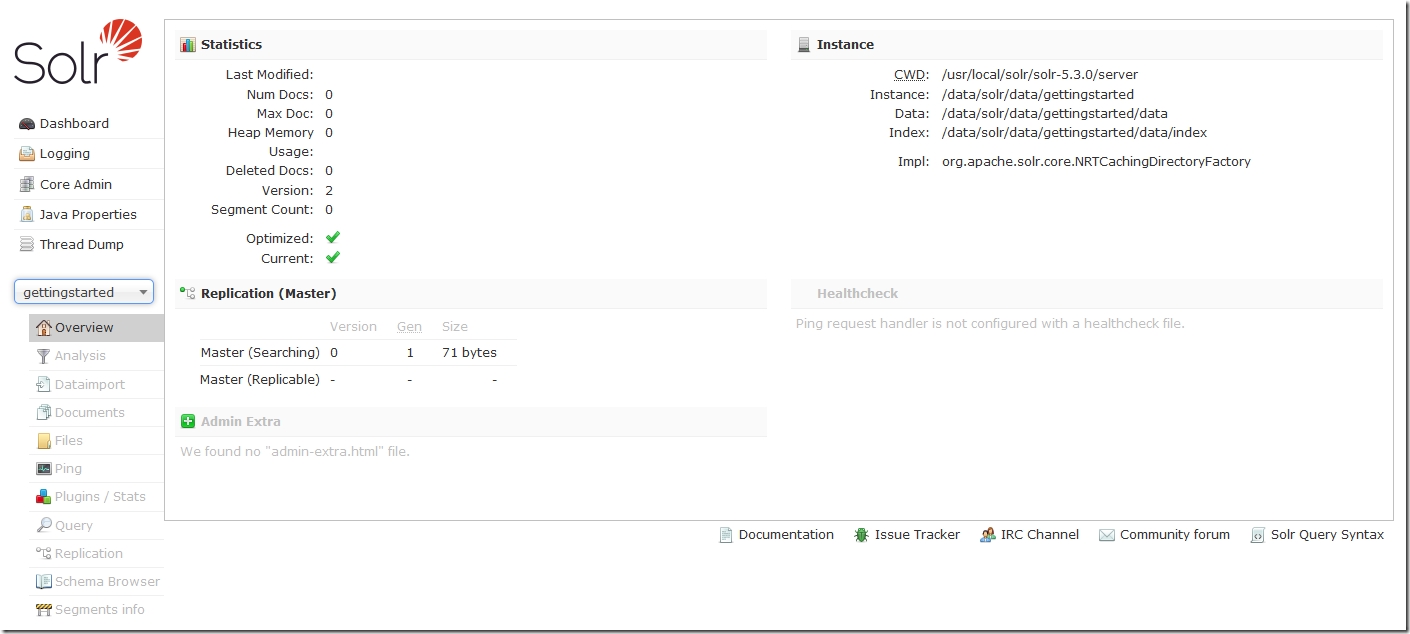
集合被划分为核,这就是为什么在Web界面中有大量的对核的参照。现在,gettingstarted只包含一个核,名为gettingstarted。在左手边,可以看到“Core Selector”下拉菜单,我们可以选择gettingstarted看到更多信息。
在选择gettingstarted核之后,选择“Documents”。文档存储可被Solr搜索的真实数据。因为我们使用了一个无模式的配置,我们可以使用任何列。我使用如下的JSON示例添加了一个单一文档,通过拷贝以下到“Documents(s)”列:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
{
"number": 1,
"president": "George Washington",
"birth_year": 1732,
"death_year": 1799,
"took_office": "1789-04-30",
"left_office": "1797-03-04",
"party": "No Party"
}
|
点击“Submit document”添加文档到索引。过一会,你会看到如下信息:
添加文档后的输出:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Status: success
Response:
{
"responseHeader": {
"status": 0,
"QTime": 290
}
}
|
你可以使用一个类似的或完全不同的结构添加更多文档,但你也可以只使用一个文档继续。
现在,选择左边的“Query”去查询我们刚刚添加的文档。保持屏幕中的默认值,在点击“Execute Query”之后,你最多看到10个文档,依赖于你添加了多少:
查询输出
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
{
"responseHeader": {
"status": 0,
"QTime": 39,
"params": {
"q": "*:*",
"indent": "true",
"wt": "json",
"_": "1442371884598"
}
},
"response": {
"numFound": 1,
"start": 0,
"docs": [
{
"number": [
1
],
"president": [
"George Washington"
],
"birth_year": [
1732
],
"death_year": [
1799
],
"took_office": [
"1789-04-30T00:00:00Z"
],
"left_office": [
"1797-03-04T00:00:00Z"
],
"party": [
"No Party"
],
"id": "b9b294c1-4b68-4d96-adc2-f6fb77f60932",
"_version_": 1512437472611532800
}
]
}
}
|
参考:http://lucene.apache.org/solr/quickstart.html
本文转自UltraSQL51CTO博客,原文链接: http://blog.51cto.com/ultrasql/1695262,如需转载请自行联系原作者