matplotlib有一个finance子模块提供了一个获取雅虎股票数据的api接口:quotes_historical_yahoo_ochl
感觉非常好用!
示例一
获取数据并作折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.finance import quotes_historical_yahoo_ochl from matplotlib.dates import YearLocator, MonthLocator, DateFormatter import datetime plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False ticker = '600028.ss' date1 = datetime.date( 2015, 1, 10 ) date2 = datetime.date( 2016, 1, 10 ) daysFmt = DateFormatter('%m-%d-%Y') quotes = quotes_historical_yahoo_ochl(ticker, date1, date2) if len(quotes) == 0: raise SystemExit print(quotes[1]) dates = [q[0] for q in quotes] opens = [q[1] for q in quotes] closes = [q[2] for q in quotes] fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.plot_date(dates, opens, '-') # format the ticks ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(daysFmt) ax.autoscale_view() # format the coords message box def price(x): return '$%1.2f'%x ax.fmt_xdata = DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d') ax.fmt_ydata = price ax.grid(True) fig.autofmt_xdate() plt.title('中国石化 600028') plt.show()
效果图:
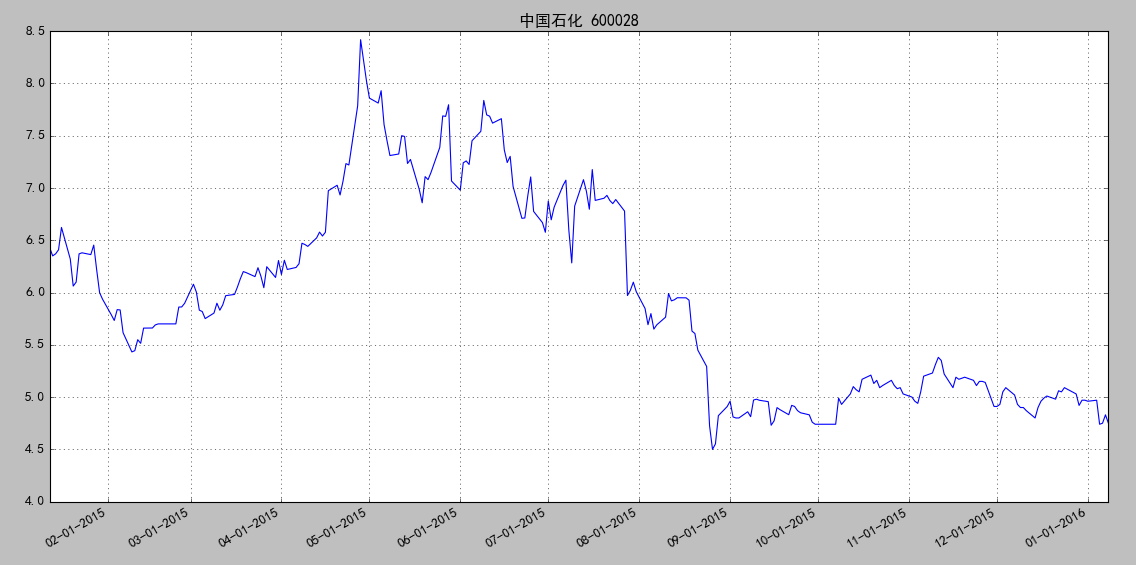
示例二
获取数据,并作蜡烛图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.dates import DateFormatter, WeekdayLocator, DayLocator, MONDAY,YEARLY from matplotlib.finance import quotes_historical_yahoo_ohlc, candlestick_ohlc plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False ticker = '600028' # 600028 是"中国石化"的股票代码 ticker += '.ss' # .ss 表示上证 .sz表示深证 date1 = (2015, 8, 1) # 起始日期,格式:(年,月,日)元组 date2 = (2016, 1, 1) # 结束日期,格式:(年,月,日)元组 mondays = WeekdayLocator(MONDAY) # 主要刻度 alldays = DayLocator() # 次要刻度 #weekFormatter = DateFormatter('%b %d') # 如:Jan 12 mondayFormatter = DateFormatter('%m-%d-%Y') # 如:2-29-2015 dayFormatter = DateFormatter('%d') # 如:12 quotes = quotes_historical_yahoo_ohlc(ticker, date1, date2) if len(quotes) == 0: raise SystemExit fig, ax = plt.subplots() fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.2) ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(mondays) ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(alldays) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mondayFormatter) #ax.xaxis.set_minor_formatter(dayFormatter) #plot_day_summary(ax, quotes, ticksize=3) candlestick_ohlc(ax, quotes, width=0.6, colorup='r', colordown='g') ax.xaxis_date() ax.autoscale_view() plt.setp(plt.gca().get_xticklabels(), rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right') ax.grid(True) plt.title('中国石化 600028') plt.show()
效果图:
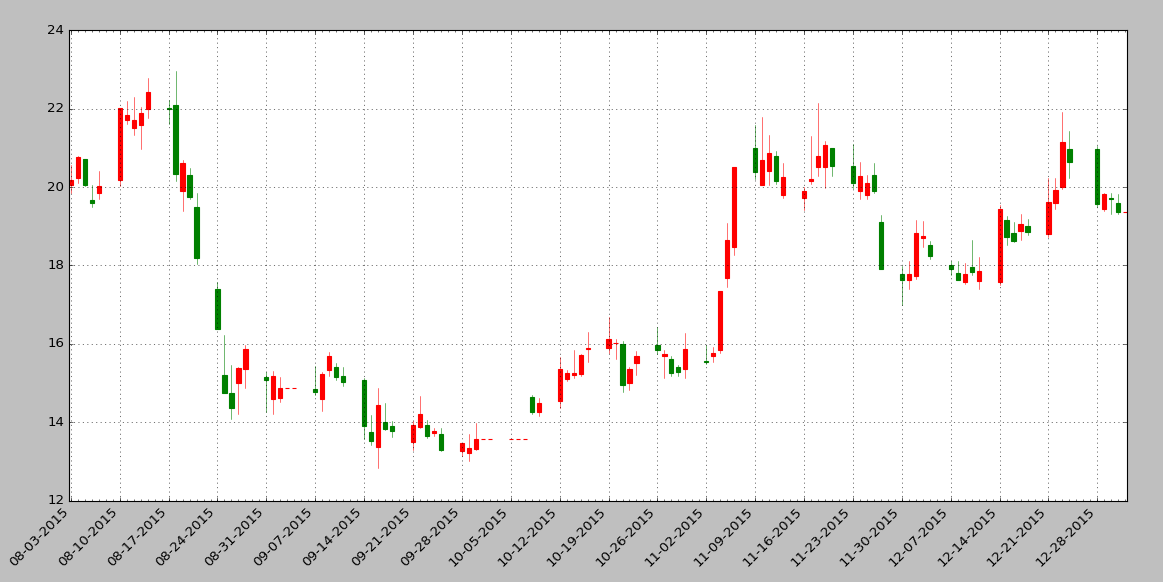
示例三
获取上证50成分股数据,进行聚类分析(看看那些股票价格关联性强),并作图
import datetime import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.finance import quotes_historical_yahoo_ochl from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection from sklearn import cluster, covariance, manifold plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False ############################################################################### # Retrieve the data from Internet # Choose a time period reasonably calm (not too long ago so that we get # high-tech firms, and before the 2008 crash) d1 = datetime.datetime(2015, 1, 1) d2 = datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 1) # 上证50成分股 symbol_dict = { "600000": "浦发银行", "600010": "包钢股份", "600015": "华夏银行", "600016": "民生银行", "600018": "上港集团", "600028": "中国石化", "600030": "中信证券", "600036": "招商银行", "600048": "保利地产", "600050": "中国联通", "600089": "特变电工", "600104": "上汽集团", "600109": "国金证券", "600111": "北方稀土", "600150": "中国船舶", "600256": "广汇能源", "600406": "国电南瑞", "600518": "康美药业", "600519": "贵州茅台", "600583": "海油工程", "600585": "海螺水泥", "600637": "东方明珠", "600690": "青岛海尔", "600837": "海通证券", "600887": "伊利股份", "600893": "中航动力", "600958": "东方证券", "600999": "招商证券", "601006": "大秦铁路", "601088": "中国神华", "601166": "兴业银行", "601169": "北京银行", "601186": "中国铁建", "601288": "农业银行", "601318": "中国平安", "601328": "交通银行", "601390": "中国中铁", "601398": "工商银行", "601601": "中国太保", "601628": "中国人寿", "601668": "中国建筑", "601688": "华泰证券", "601766": "中国中车", "601800": "中国交建", "601818": "光大银行", "601857": "中国石油", "601901": "方正证券", "601988": "中国银行", "601989": "中国重工", "601998": "中信银行"} symbols, names = np.array(list(symbol_dict.items())).T quotes = [quotes_historical_yahoo_ochl(symbol+".ss", d1, d2, asobject=True) for symbol in symbols] open = np.array([q.open for q in quotes]).astype(np.float) close = np.array([q.close for q in quotes]).astype(np.float) # 每日价格浮动包含了重要信息! variation = close - open ############################################################################### # Learn a graphical structure from the correlations edge_model = covariance.GraphLassoCV() # standardize the time series: using correlations rather than covariance # is more efficient for structure recovery X = variation.copy().T X /= X.std(axis=0) edge_model.fit(X) ############################################################################### # Cluster using affinity propagation _, labels = cluster.affinity_propagation(edge_model.covariance_) n_labels = labels.max() for i in range(n_labels + 1): print('Cluster %i: %s' % ((i + 1), ', '.join(names[labels == i]))) ############################################################################### # Find a low-dimension embedding for visualization: find the best position of # the nodes (the stocks) on a 2D plane # We use a dense eigen_solver to achieve reproducibility (arpack is # initiated with random vectors that we don't control). In addition, we # use a large number of neighbors to capture the large-scale structure. node_position_model = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding( n_components=2, eigen_solver='dense', n_neighbors=6) embedding = node_position_model.fit_transform(X.T).T ############################################################################### # Visualization plt.figure(1, facecolor='w', figsize=(10, 8)) plt.clf() ax = plt.axes([0., 0., 1., 1.]) plt.axis('off') # Display a graph of the partial correlations partial_correlations = edge_model.precision_.copy() d = 1 / np.sqrt(np.diag(partial_correlations)) partial_correlations *= d partial_correlations *= d[:, np.newaxis] non_zero = (np.abs(np.triu(partial_correlations, k=1)) > 0.02) # Plot the nodes using the coordinates of our embedding plt.scatter(embedding[0], embedding[1], s=100 * d ** 2, c=labels, cmap=plt.cm.spectral) # Plot the edges start_idx, end_idx = np.where(non_zero) #a sequence of (*line0*, *line1*, *line2*), where:: # linen = (x0, y0), (x1, y1), ... (xm, ym) segments = [[embedding[:, start], embedding[:, stop]] for start, stop in zip(start_idx, end_idx)] values = np.abs(partial_correlations[non_zero]) lc = LineCollection(segments, zorder=0, cmap=plt.cm.hot_r, norm=plt.Normalize(0, .7 * values.max())) lc.set_array(values) lc.set_linewidths(15 * values) ax.add_collection(lc) # Add a label to each node. The challenge here is that we want to # position the labels to avoid overlap with other labels for index, (name, label, (x, y)) in enumerate( zip(names, labels, embedding.T)): dx = x - embedding[0] dx[index] = 1 dy = y - embedding[1] dy[index] = 1 this_dx = dx[np.argmin(np.abs(dy))] this_dy = dy[np.argmin(np.abs(dx))] if this_dx > 0: horizontalalignment = 'left' x = x + .002 else: horizontalalignment = 'right' x = x - .002 if this_dy > 0: verticalalignment = 'bottom' y = y + .002 else: verticalalignment = 'top' y = y - .002 plt.text(x, y, name, size=10, horizontalalignment=horizontalalignment, verticalalignment=verticalalignment, bbox=dict(facecolor='w', edgecolor=plt.cm.spectral(label / float(n_labels)), alpha=.6)) plt.xlim(embedding[0].min() - .15 * embedding[0].ptp(), embedding[0].max() + .10 * embedding[0].ptp(),) plt.ylim(embedding[1].min() - .03 * embedding[1].ptp(), embedding[1].max() + .03 * embedding[1].ptp()) plt.title('上证50成分股') plt.show()
效果图:
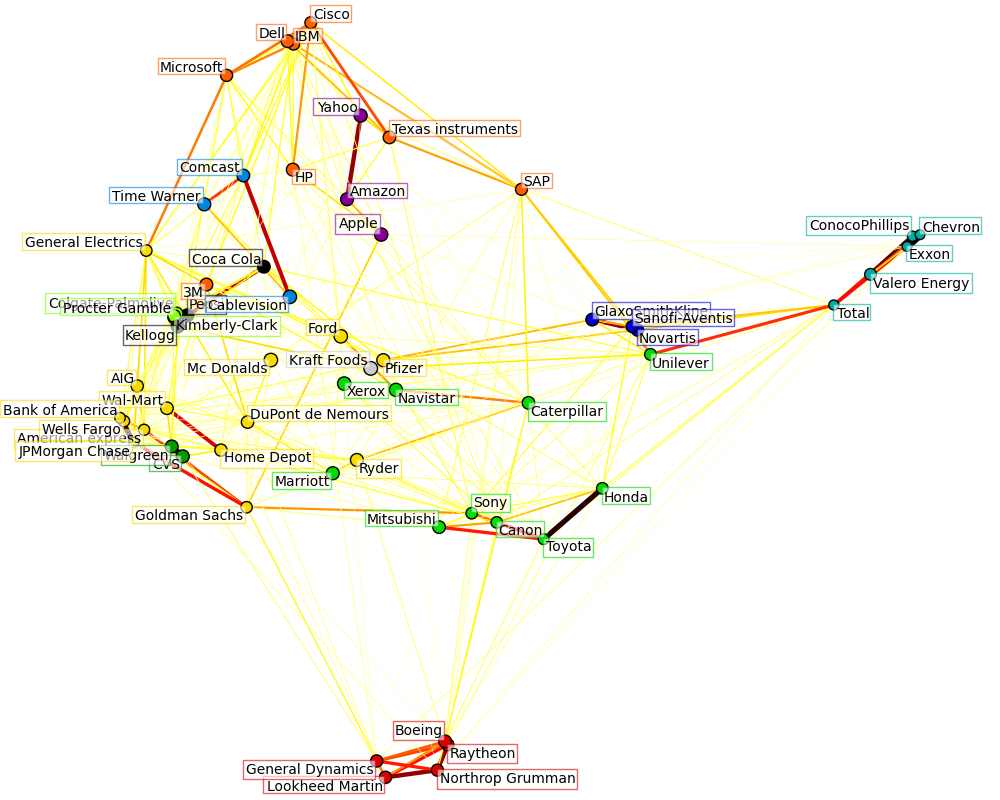
说明:
这个图是原例子的图,统计的是美股60只股票,我用原例运行是可以的。
但是我换成上证50成分股后,雅虎拒绝我的的连接,所以下载不了数据,因此就看不到效果!
抱歉了各位朋友。
有图为证:

另:
示例四
下载雅虎股票数据到本地保存
import os import urllib.request ''' 雅虎历史数据请求 请求地址:http://ichart.yahoo.com/table.csv?s=string&a=int&b=int&c=int&d=int&e=int&f=int&g=d&ignore=.csv 或者:http://table.finance.yahoo.com/table.csv?a=%d&b=%d&c=%d&d=%d&e=%d&f=%d&s=%s&y=0&g=%s&ignore=.csv 两者参数有点不一样 说明: s — 股票名称 a — 起始时间,月 b — 起始时间,日 c — 起始时间,年 d — 结束时间,月 e — 结束时间,日 f — 结束时间,年 g — 时间周期。 Ø 参数g的取值范围:d->‘日’(day), w->‘周’(week),m->‘月’(mouth),v->‘dividends only’ Ø 月份是从0开始的,如9月数据,则写为08。 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< 示例 查询浦发银行2010.09.25 – 2010.10.8之间日线数据 http://ichart.yahoo.com/table.csv?s=600000.SS&a=08&b=25&c=2010&d=09&e=8&f=2010&g=d 查看国内沪深股市的股票,规则是:沪股代码末尾加.ss,深股代码末尾加.sz。如浦发银行的代号是:600000.SS ''' ticker = '600028' # 600028 是"中国石化"的股票代码 ticker += '.ss' # .ss 表示上证 .sz表示深证 date1 = ( 2015, 1, 1 ) #begining time date2 = ( 2016, 1, 1 ) #ending time d1 = (date1[1]-1, date1[2], date1[0]) d2 = (date2[1]-1, date2[2], date2[0]) g='d' urlFmt = 'http://table.finance.yahoo.com/table.csv?a=%d&b=%d&c=%d&d=%d&e=%d&f=%d&s=%s&y=0&g=%s&ignore=.csv' url = urlFmt % (d1[0], d1[1], d1[2], d2[0], d2[1], d2[2], ticker, g) #the url of historical data filename = 'data.csv' #file name filename = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), filename) #located file
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename) #下载,保存
本文转自罗兵博客园博客,原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/hhh5460/p/5120079.html
,如需转载请自行联系原作者
