目前python 提供了几种多线程实现方式 thread,threading,
multithreading
,其中thread模块比较底层,而threading模块是对thread做了一些包装,可以更加方便的被使用。
2.7版本之前python对线程的支持还不够完善,不能利用多核CPU,但是2.7版本的python中已经考虑改进这点,出现了 multithreading 模块。threading模块里面主要是对一些线程的操作对象化,创建Thread的class。一般来说,使用线程有两种模式:
A 创建线程要执行的函数,把这个函数传递进Thread对象里,让它来执行;
B 继承Thread类,创建一个新的class,将要执行的代码 写到run函数里面。
本文介绍两种实现方法。
第一种 创建函数并且传入Thread 对象 中
t.py 脚本内容
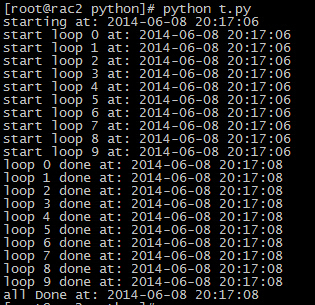
执行结果:
thclass.py 脚本内容:
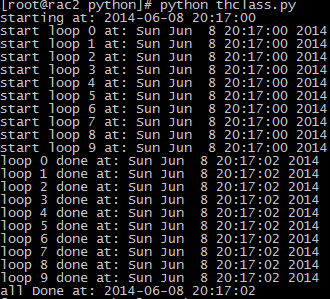
执行结果:
2.7版本之前python对线程的支持还不够完善,不能利用多核CPU,但是2.7版本的python中已经考虑改进这点,出现了 multithreading 模块。threading模块里面主要是对一些线程的操作对象化,创建Thread的class。一般来说,使用线程有两种模式:
A 创建线程要执行的函数,把这个函数传递进Thread对象里,让它来执行;
B 继承Thread类,创建一个新的class,将要执行的代码 写到run函数里面。
本文介绍两种实现方法。
第一种 创建函数并且传入Thread 对象 中
t.py 脚本内容
- import threading,time
- from time import sleep, ctime
- def now() :
- return str( time.strftime( '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' , time.localtime() ) )
-
- def test(nloop, nsec):
- print 'start loop', nloop, 'at:', now()
- sleep(nsec)
- print 'loop', nloop, 'done at:', now()
-
- def main():
- print 'starting at:',now()
- threadpool=[]
-
- for i in xrange(10):
- th = threading.Thread(target= test,args= (i,2))
- threadpool.append(th)
-
- for th in threadpool:
- th.start()
-
- for th in threadpool :
- threading.Thread.join( th )
-
- print 'all Done at:', now()
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()

thclass.py 脚本内容:
- import threading ,time
- from time import sleep, ctime
- def now() :
- return str( time.strftime( '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' , time.localtime() ) )
-
- class myThread (threading.Thread) :
- """docstring for myThread"""
- def __init__(self, nloop, nsec) :
- super(myThread, self).__init__()
- self.nloop = nloop
- self.nsec = nsec
-
- def run(self):
- print 'start loop', self.nloop, 'at:', ctime()
- sleep(self.nsec)
- print 'loop', self.nloop, 'done at:', ctime()
- def main():
- thpool=[]
- print 'starting at:',now()
-
- for i in xrange(10):
- thpool.append(myThread(i,2))
-
- for th in thpool:
- th.start()
-
- for th in thpool:
- th.join()
-
- print 'all Done at:', now()
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
