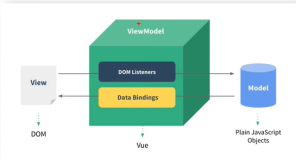
双向数据绑定
双向绑定意味着当我们更改name的值时会更新input输入框的值,更改input输入框值的时候name的值同样会改变。
<script>
let name = 'world';
</script>
<input bind:value={name}>
<h1>Hello {name}!</h1>如果您有多个与同一个值相关的输入,则可以bind:group与value属性一起使用。同一组中的单选框是互斥的;同一组中的复选框输入形成选定值的数组。
<script>
let scoops=1
let flavours = ['Mint choc chip'];
let menu = [
'Cookies and cream',
'Mint choc chip',
'Raspberry ripple'
];
</script>
<label>
<input type=radio bind:group={scoops} value={1}>
One scoop
</label>
<label>
<input type=radio bind:group={scoops} value={2}>
Two scoops
</label>
<label>
<input type=radio bind:group={scoops} value={3}>
Three scoops
</label>
<div>
{#each menu as flavour}
<label>
<input type=checkbox bind:group={flavours} value={flavour}>
{flavour}
</label>
{/each}
</div>我们还可以使用bind:value与元素绑定:
<script>
let questions = [
{ id: 1, text: `Where did you go to school?` },
{ id: 2, text: `What is your mother's name?` },
{
id: 3,
text: `What is another personal fact that an attacker could easily find with Google?`
}
];
let selected;
</script>
<select bind:value={selected}>
{#each questions as question}
<option value={question.id} label={question.text}></option>
{/each}
</select>
<p>The question is "{selected?questions.filter(q => q.id === selected)[0].text:null}"</p>
的value值也可以是对象
<script>
let questions = [
{ id: 1, text: `Where did you go to school?` },
{ id: 2, text: `What is your mother's name?` },
{
id: 3,
text: `What is another personal fact that an attacker could easily find with Google?`
}
];
let selected;
</script>
<select bind:value={selected}>
{#each questions as question}
<option value={question} label={question.text}></option>
{/each}
</select>
<p>The question is "{selected?selected.text:''}"</p>
一个可以具有一个multiple属性,在这种情况下,它将绑定一个数组而不是一个值。
<script>
let questions = [
{ id: 1, text: `Where did you go to school?` },
{ id: 2, text: `What is your mother's name?` },
{
id: 3,
text: `What is another personal fact that an attacker could easily find with Google?`
}
];
let selectedList = [];
</script>
<select bind:value={selectedList} multiple>
{#each questions as question}
<option value={question} label={question.text} />
{/each}
</select>
{#each selectedList as selected}
<p>The question is "{selected.text}"</p>
{/each}
contenteditable
具有contenteditable="true"属性的元素支持绑定textContent和innerHTML。
<script>
let html = "<p>Write some text!</p>";
let text = "Write some text!";
</script>
<style>
[contenteditable] {
padding: 0.5em;
border: 1px solid #eee;
border-radius: 4px;
}
</style>
<div contenteditable="true" bind:innerHTML={html} />
<div contenteditable="true" bind:textContent={text} />
<pre>{html}</pre>
<p>{text}</p>
循环中使用数据绑定
<script>
let todos = [
{ done: false, text: 'finish Svelte tutorial' },
{ done: false, text: 'build an app' },
{ done: false, text: 'world domination' }
];
function add() {
todos = todos.concat({ done: false, text: '' });
}
function clear() {
todos = todos.filter(t => !t.done);
}
$: remaining = todos.filter(t => !t.done).length;
</script>
<style>
.done {
opacity: 0.4;
}
</style>
<h1>Todos</h1>
{#each todos as todo}
<div class:done={todo.done}>
<input
type=checkbox
bind:checked={todo.done}
>
<input
placeholder="What needs to be done?"
bind:value={todo.text}
>
</div>
{/each}
<p>{remaining} remaining</p>
<button on:click={add}>
Add new
</button>
<button on:click={clear}>
Clear completed
</button>
clientWidth、clientHeight、offsetWidth、offsetHeight
这些属性为只读属性改变w、h的值不会更新元素。inline元素没有宽高。
<script>
let w;
let h;
let w2;
let h2;
let size = 42;
let text = "edit me";
</script>
<style>
input {
display: block;
margin: 20px auto;
}
div {
display: block;
}
.inline {
display: inline;
}
</style>
<input type="range" bind:value={size} />
<input bind:value={text} />
<p>size: {w}px x {h}px</p>
<div bind:clientWidth={w} bind:clientHeight={h}>
<span style="font-size: {size}px">{text}</span>
</div>
<p>line size: {w2}px x {h2}px</p>
<div bind:clientWidth={w2} bind:clientHeight={h2} class="inline">
<span style="font-size: {size}px">{text}</span>
</div>
bind:this
bind:this可以拿到一个元素的引用。
<script>
let w;
let h;
let w2;
let h2;
let size = 42;
let text = "edit me";
function getRects(){
console.log(this.getClientRects())
console.log(this.getBoundingClientRect())
}
</script>
<style>
input {
display: block;
margin: 20px auto;
}
div {
display: block;
}
.inline {
display: inline;
}
</style>
<input type="range" bind:value={size} />
<input bind:value={text} />
<p>size: {w}px x {h}px</p>
<div
on:click={getRects}
bind:clientWidth={w}
bind:clientHeight={h}>
<span style="font-size: {size}px">{text}</span>
</div>
<p>line size: {w2}px x {h2}px</p>
<div
on:click={getRects}
bind:clientWidth={w2}
bind:clientHeight={h2}
class="inline">
<span style="font-size: {size}px">
{text}
</span>
</div>组件数据绑定
正如可以绑定到DOM元素的属性一样,也可以绑定到组件prop。
// Keypad.svelte
<script>
import { createEventDispatcher } from "svelte";
export let value = "";
const dispatch = createEventDispatcher();
const select = num => () => (value += num);
const clear = () => (value = "");
const submit = () => dispatch("submit");
</script>
<style>
.keypad {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 5em);
grid-template-rows: repeat(4, 3em);
grid-gap: 0.5em;
justify-content: center;
}
button {
margin: 0;
}
</style>
<div class="keypad">
<button on:click={select(1)}>1</button>
<button on:click={select(2)}>2</button>
<button on:click={select(3)}>3</button>
<button on:click={select(4)}>4</button>
<button on:click={select(5)}>5</button>
<button on:click={select(6)}>6</button>
<button on:click={select(7)}>7</button>
<button on:click={select(8)}>8</button>
<button on:click={select(9)}>9</button>
<button disabled={!value} on:click={clear}>clear</button>
<button on:click={select(0)}>0</button>
<button disabled={!value} on:click={submit}>submit</button>
</div>
// component_bind.svelte
<script>
import Keypad from '../components/Keypad';
let pin;
$: view = pin ? pin.replace(/\d(?!$)/g, '•') : 'enter your pin';
function handleSubmit() {
alert(`submitted ${pin}`);
}
</script>
<h1 style="color: {pin ? '#333' : '#ccc'}">{view}</h1>
<Keypad bind:value={pin} on:submit={handleSubmit}/>本教程的所有代码均上传到github有需要的同学可以参考 https://github.com/sullay/svelte-learn。