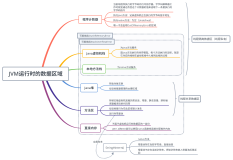
程序计算时间:
longstartTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
。。。。。。。。。。。。
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
System.out.println("程序运行时间: "+(endTime-startTime)+"ms(毫秒)");
利用java程序实现获取计算机cpu利用率和内存使用信息。
创建一个Bean用来存贮要得到的信
public class MonitorInfoBean {
private longtotalMemory;
private longfreeMemory;
private longmaxMemory;
privateString osName;
private longtotalMemorySize;
private longfreePhysicalMemorySize;
private longusedMemory;
private inttotalThread;
privatedouble cpuRatio;
public longgetFreeMemory() {
return freeMemory;
}
public voidsetFreeMemory(long freeMemory) {
this.freeMemory = freeMemory;
}
public longgetFreePhysicalMemorySize() {
return freePhysicalMemorySize;
}
public voidsetFreePhysicalMemorySize(long freePhysicalMemorySize){
this.freePhysicalMemorySize =freePhysicalMemorySize;
}
public longgetMaxMemory() {
return maxMemory;
}
public voidsetMaxMemory(long maxMemory) {
this.maxMemory = maxMemory;
}
publicString getOsName() {
return osName;
}
public voidsetOsName(String osName) {
this.osName = osName;
}
public longgetTotalMemory() {
return totalMemory;
}
public voidsetTotalMemory(long totalMemory) {
this.totalMemory = totalMemory;
}
public longgetTotalMemorySize() {
return totalMemorySize;
}
public voidsetTotalMemorySize(long totalMemorySize) {
this.totalMemorySize = totalMemorySize;
}
public intgetTotalThread() {
return totalThread;
}
public voidsetTotalThread(int totalThread) {
this.totalThread = totalThread;
}
public longgetUsedMemory() {
return usedMemory;
}
public voidsetUsedMemory(long usedMemory) {
this.usedMemory = usedMemory;
}
publicdouble getCpuRatio() {
return cpuRatio;
}
public voidsetCpuRatio(double cpuRatio) {
this.cpuRatio = cpuRatio;
}
}
之后,建立bean的接口
public interface IMonitorService {
publicMonitorInfoBean getMonitorInfoBean() throwsException;
}
然后,就是最关键的,得到cpu的利用率,已用内存,可用内存,最大内存等信息。
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.LineNumberReader;
import sun.management.ManagementFactory;
import com.sun.management.OperatingSystemMXBean;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class MonitorServiceImpl implements IMonitorService{
privatestatic final int CPUTIME = 30;
privatestatic final int PERCENT = 100;
privatestatic final int FAULTLENGTH = 10;
privatestatic final File versionFile = newFile("/proc/version");
privatestatic String linuxVersion = null;
publicMonitorInfoBean getMonitorInfoBean() throws Exception{
int kb = 1024;
// 可使用内存
long totalMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() /kb;
// 剩余内存
long freeMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory() /kb;
// 最大可使用内存
long maxMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() /kb;
OperatingSystemMXBean osmxb = (OperatingSystemMXBean)ManagementFactory
.getOperatingSystemMXBean();
// 操作系统
String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");
// 总的物理内存
long totalMemorySize = osmxb.getTotalPhysicalMemorySize() /kb;
// 剩余的物理内存
long freePhysicalMemorySize = osmxb.getFreePhysicalMemorySize() /kb;
// 已使用的物理内存
long usedMemory = (osmxb.getTotalPhysicalMemorySize() -osmxb
.getFreePhysicalMemorySize())
/ kb;
// 获得线程总数
ThreadGroup parentThread;
for (parentThread = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();parentThread
.getParent() != null; parentThread =parentThread.getParent())
;
int totalThread = parentThread.activeCount();
double cpuRatio = 0;
if (osName.toLowerCase().startsWith("windows")) {
cpuRatio = this.getCpuRatioForWindows();
}
else {
cpuRatio = this.getCpuRateForLinux();
}
// 构造返回对象
MonitorInfoBean infoBean = new MonitorInfoBean();
infoBean.setFreeMemory(freeMemory);
infoBean.setFreePhysicalMemorySize(freePhysicalMemorySize);
infoBean.setMaxMemory(maxMemory);
infoBean.setOsName(osName);
infoBean.setTotalMemory(totalMemory);
infoBean.setTotalMemorySize(totalMemorySize);
longstartTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
。。。。。。。。。。。。
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
System.out.println("程序运行时间: "+(endTime-startTime)+"ms(毫秒)");
利用java程序实现获取计算机cpu利用率和内存使用信息。
创建一个Bean用来存贮要得到的信
public class MonitorInfoBean {
private longtotalMemory;
private longfreeMemory;
private longmaxMemory;
privateString osName;
private longtotalMemorySize;
private longfreePhysicalMemorySize;
private longusedMemory;
private inttotalThread;
privatedouble cpuRatio;
public longgetFreeMemory() {
return freeMemory;
}
public voidsetFreeMemory(long freeMemory) {
this.freeMemory = freeMemory;
}
public longgetFreePhysicalMemorySize() {
return freePhysicalMemorySize;
}
public voidsetFreePhysicalMemorySize(long freePhysicalMemorySize){
this.freePhysicalMemorySize =freePhysicalMemorySize;
}
public longgetMaxMemory() {
return maxMemory;
}
public voidsetMaxMemory(long maxMemory) {
this.maxMemory = maxMemory;
}
publicString getOsName() {
return osName;
}
public voidsetOsName(String osName) {
this.osName = osName;
}
public longgetTotalMemory() {
return totalMemory;
}
public voidsetTotalMemory(long totalMemory) {
this.totalMemory = totalMemory;
}
public longgetTotalMemorySize() {
return totalMemorySize;
}
public voidsetTotalMemorySize(long totalMemorySize) {
this.totalMemorySize = totalMemorySize;
}
public intgetTotalThread() {
return totalThread;
}
public voidsetTotalThread(int totalThread) {
this.totalThread = totalThread;
}
public longgetUsedMemory() {
return usedMemory;
}
public voidsetUsedMemory(long usedMemory) {
this.usedMemory = usedMemory;
}
publicdouble getCpuRatio() {
return cpuRatio;
}
public voidsetCpuRatio(double cpuRatio) {
this.cpuRatio = cpuRatio;
}
}
之后,建立bean的接口
public interface IMonitorService {
publicMonitorInfoBean getMonitorInfoBean() throwsException;
}
然后,就是最关键的,得到cpu的利用率,已用内存,可用内存,最大内存等信息。
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.LineNumberReader;
import sun.management.ManagementFactory;
import com.sun.management.OperatingSystemMXBean;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class MonitorServiceImpl implements IMonitorService{
privatestatic final int CPUTIME = 30;
privatestatic final int PERCENT = 100;
privatestatic final int FAULTLENGTH = 10;
privatestatic final File versionFile = newFile("/proc/version");
privatestatic String linuxVersion = null;
publicMonitorInfoBean getMonitorInfoBean() throws Exception{
int kb = 1024;
// 可使用内存
long totalMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() /kb;
// 剩余内存
long freeMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory() /kb;
// 最大可使用内存
long maxMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() /kb;
OperatingSystemMXBean osmxb = (OperatingSystemMXBean)ManagementFactory
.getOperatingSystemMXBean();
// 操作系统
String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");
// 总的物理内存
long totalMemorySize = osmxb.getTotalPhysicalMemorySize() /kb;
// 剩余的物理内存
long freePhysicalMemorySize = osmxb.getFreePhysicalMemorySize() /kb;
// 已使用的物理内存
long usedMemory = (osmxb.getTotalPhysicalMemorySize() -osmxb
.getFreePhysicalMemorySize())
/ kb;
// 获得线程总数
ThreadGroup parentThread;
for (parentThread = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();parentThread
.getParent() != null; parentThread =parentThread.getParent())
;
int totalThread = parentThread.activeCount();
double cpuRatio = 0;
if (osName.toLowerCase().startsWith("windows")) {
cpuRatio = this.getCpuRatioForWindows();
}
else {
cpuRatio = this.getCpuRateForLinux();
}
// 构造返回对象
MonitorInfoBean infoBean = new MonitorInfoBean();
infoBean.setFreeMemory(freeMemory);
infoBean.setFreePhysicalMemorySize(freePhysicalMemorySize);
infoBean.setMaxMemory(maxMemory);
infoBean.setOsName(osName);
infoBean.setTotalMemory(totalMemory);
infoBean.setTotalMemorySize(totalMemorySize);